Apraclonidine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Iopidine |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a608005 |
| Routes of administration | Topical (ophthalmic solution) |
| ATC code | S01EA03 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 98.7% |
| Biological half-life | 8 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
66711-21-5 |
| PubChem (CID) | 2216 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 7117 |
| DrugBank |
DB00964 |
| ChemSpider |
2130 |
| UNII |
843CEN85DI |
| KEGG |
D07461 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:2788 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL647 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
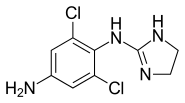
| Formula | C9H10Cl2N4 |
| Molar mass | 245.108 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Apraclonidine (INN), also known under the brand name Iopidine, is a sympathomimetic used in glaucoma therapy. It is an α2 adrenergic receptor agonist and a weak α1 adrenergic receptor agonist.
Topical apraclonidine is administered at a concentration of 1% for the prevention and treatment of post-surgical intraocular pressure (IOP) elevation and 0.5% for short-term adjunctive therapy in patients on maximally tolerated medical therapy who require additional reduction of IOP. One drop is usually added one hour prior to laser eye surgery and another drop is given after the procedure is complete.
Clinical uses
Apraclonidine is indicated for the short-term adjunctive treatment of glaucoma for patients on maximally tolerated medical therapy who require additional reduction of IOP. These patients, who are treated with apraclonidine to delay surgery, should have frequent follow-up examinations and treatment should be discontinued if the intraocular pressure rises significantly.
Apraclonidine may be useful in the diagnosis of Horner's syndrome. In Horner's syndrome, the sympathetic innervation to the pupillary dilator muscle is lost. The affected pupil is thus miotic and the pupillary dilator responds to denervation by increasing α1 receptors. Apraclonidine is useful in this case due to its weak α1-adrenergic properties. When applied to the denervated (and thus hyper-sensitive) pupillary dilator muscle, a super-normal dilatory response is generated in which the pupil dilates to a degree greater than that which would be seen in a non-denervated muscle. This causes the reversal of anisocoria that is characteristic of Horner's.
Topical apraclonidine can also decrease IOP in glaucoma patients by increasing trabecular outflow, in a similar way to clonidine,[1] but without the cardiovascular side effects.
External links
- Iopidine prescribing information (from the FDA website)
References
- ↑ Toris, C. B.; Tafoya, M. E.; Camras, C. B.; Yablonski, M. E. (1995). "Effects of Apraclonidine on Aqueous Humor Dynamics in Human Eyes". Ophthalmology. 102 (3): 456. doi:10.1016/S0161-6420(95)31000-7.
- Chen P, Chen J, Lu D, Chen Y, Hsiao C (2006). "Comparing efficacies of 0.5% apraclonidine with 4% cocaine in the diagnosis of horner syndrome in pediatric patients". J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 22 (3): 182–7. doi:10.1089/jop.2006.22.182. PMID 16808679.
- Aslanides l; Tsiklis N; Ozkilic E; Coskunseven E; Pallikaris l; Jankov M (2006). "The effect of topical apraclonidine on subconjunctival hemorrhage and flap adherence in LASIK patients". J Refract Surg. 22 (6): 585–8. PMID 16805122.
- Koc F, Kansu T, Kavuncu S, Firat E (2006). "Topical apraclonidine testing discloses pupillary sympathetic denervation in diabetic patients". J Neuroophthalmol. 26 (1): 25–9. doi:10.1097/01.wno.0000204648.79744.71. PMID 16518162.
- Garibaldi D, Hindman H, Grant M, Iliff N, Merbs S (2006). "Effect of 0.5% apraclonidine on ptosis in Horner syndrome". Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 22 (1): 53–5. doi:10.1097/01.iop.0000196322.05586.6a. PMID 16418668.
- Onal S, Gozum N, Gucukoglu A (2005). "Effect of apraclonidine versus dorzolamide on intraocular pressure after phacoemulsification". Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 36 (6): 457–62. PMID 16355950.