Leuprorelin
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Lupron, Eligard, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| MedlinePlus | a685040 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Implant / Injection |
| ATC code | L02AE02 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Biological half-life | 3 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms | leuprolide (USAN) |
| CAS Number |
53714-56-0 74381-53-6 (acetate) |
| PubChem (CID) | 441410 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 1175 |
| DrugBank |
DB00007 |
| ChemSpider |
571356 |
| UNII |
EFY6W0M8TG |
| KEGG |
D08113 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1201199 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.161.466 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C59H84N16O12 |
| Molar mass | 1209.4 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Leuprorelin, marketed under the brand name Lupron among others,[1][2][3] is a gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analogue. It is used to treat prostate cancer and breast cancer. It is used in form of the acetate salt.
It is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, the most important medications needed in a basic health system.[4]
Medical uses
An LH-RH (GnRH) analog, leuprorelin may be used in the treatment of hormone-responsive cancers such as prostate cancer or breast cancer, estrogen-dependent conditions (such as endometriosis[5] or uterine fibroids), to treat precocious puberty,[6] and to prevent premature ovulation in cycles of controlled ovarian stimulation for In Vitro Fertilization (IVF). It is considered a possible treatment for paraphilias.[7]
Leuprorelin has been tested as a treatment for reducing sexual urges in pedophiles and other cases of paraphilia.[8][9]
As of 2006 leuprorelin was under investigation for possible use in the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease.[10]
It is also used for treatment of steroid abuse.
Leuprorelin, along with triptorelin and goserelin, are often used to delay puberty in transgender youth until they are old enough to begin hormone replacement therapy.[11] They are also sometimes used as superior alternatives to anti-androgens like spironolactone and cyproterone acetate for suppressing testosterone production in trans women.
Adverse effects
Common side effects of Lupron Injection include redness/burning/stinging/pain/bruising at the injection site, hot flashes (flushing), increased sweating, night sweats, tiredness, headache, upset stomach, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, stomach pain, breast swelling or tenderness, acne, joint/muscle aches or pain, trouble sleeping (insomnia), reduced sexual interest, vaginal discomfort/dryness/itching/discharge, vaginal bleeding, swelling of the ankles/feet, increased urination at night, dizziness, breakthrough bleeding in a female child during the first 2 months of leuprorelin treatment, weakness, chills, clammy skin, skin redness, itching, or scaling, testicle pain, impotence, depression, or memory problems.[12]
Mechanism of action
Leuprorelin acts as an agonist at pituitary GnRH receptors. By interrupting the normal pulsatile stimulation of, and thus desensitizing, the GnRH receptors, it indirectly downregulates the secretion of gonadotropins luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), leading to hypogonadism and thus a dramatic reduction in estradiol and testosterone levels in both sexes.[13][14]
Chemical properties
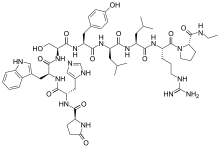
The peptide sequence is Pyr-His-Trp-Ser-Tyr-D-Leu-Leu-Arg-Pro-NHEt (Pyr = L-Pyroglutamyl).
History
Approvals
- Lupron Injection (5 mg/ml for daily subcutaneous injection) was first approved by the FDA for treatment of advanced prostate cancer on April 9, 1985.
- Lupron Depot (7.5 mg/vial for monthly intramuscular depot injection) was first approved by the FDA for palliative treatment of advanced prostate cancer on January 26, 1989, and subsequently in 22.5 mg/vial and 30 mg/vial for intramuscular depot injection every 3 and 4 months, respectively. 3.75 mg/vial and 11.25 mg/vial dosage forms were subsequently approved for subcutaneous depot injection every month and every 3 months, respectively for treatment of endometriosis or fibroids. 7.5 mg/vial, 11.25 mg/vial, and 15 mg/vial dosage forms were subsequently approved for subcutaneous depot injection for treatment of children with central precocious puberty.
- Viadur (72 mg yearly subcutaneous implant) was first approved by the FDA for palliative treatment of advanced prostate cancer on March 6, 2000. Bayer will fulfill orders until current supplies are depleted, expected by the end of April 2008
- Eligard (7.5 mg for monthly subcutaneous depot injection) was first approved by the FDA for palliative treatment of advanced prostate cancer on January 24, 2002, and subsequently in 22.5 mg, 30 mg, and 45 mg doses for subcutaneous depot injection every 3, 4, and 6 months, respectively.
- Leupromer 7.5 (7.5 mg, One month depot for subcutaneous injection) is the second In-situ forming injectable drug in the world. It is used for palliative treatment of advanced prostate cancer, endometriosis and fibroids. It was approved by The Ministry of Health and Medical Education Of Iran.
Leuprorelin is marketed by Bayer AG under the brand name Viadur, by Tolmar under the brand name Eligard, and by TAP Pharmaceuticals (1985–2008), by Varian Darou Pajooh under the brand name Leupromer and Abbott Laboratories (2008-current) under the brand name Lupron. It is available as a slow-release implant or subcutaneous/intramuscular injection.
In the UK and Ireland, leuprorelin is marketed by Takeda UK as Prostap SR (one-month injection) and Prostap 3 (three-month injection).
Society and culture
"Lupron protocol"
A 2005 paper suggested leuprorelin as a possible treatment for autism,[15] the hypothetical method of action being the now defunct hypothesis that autism is caused by mercury, with the additional unfounded assumption that mercury binds irreversibly to testosterone and therefore leuprorelin can help cure autism by lowering the testosterone levels and thereby mercury levels.[16] However there is no scientifically valid or reliable research to show its effectiveness in treating autism.[17] This use has been termed the "Lupron protocol"[18] and Mark Geier, the proponent of the hypothesis, has frequently been barred from testifying in vaccine-autism related cases on the grounds of not being sufficiently expert in that particular issue[19][20][21] and has had his medical license revoked.[18] Medical experts have referred to Geier's claims as "junk science".[22]
Veterinary use
Leuprorelin has been used in two cases of ferrets with chronic adrenal disease, one with primary hyperaldosteronism,[23] and one with hyperadrenocorticism [24]
See also
- National Women's Health Network article on Lupron Depot from November & December 2008 - "Lupron - What Does It Do To Women's Health"[25]
References
- ↑ Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 599–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- ↑ J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. p. 731. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ↑ I.K. Morton; Judith M. Hall (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 164–. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1.
- ↑ "19th WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (April 2015)" (PDF). WHO. April 2015. Retrieved May 10, 2015.
- ↑ Crosignani PG, Luciano A, Ray A, Bergqvist A (January 2006). "Subcutaneous depot medroxyprogesterone acetate versus leuprolide acetate in the treatment of endometriosis-associated pain". Human reproduction (Oxford, England). 21 (1): 248–56. doi:10.1093/humrep/dei290. PMID 16176939.
- ↑ Badaru A, Wilson DM, Bachrach LK, et al. (May 2006). "Sequential comparisons of one-month and three-month depot leuprolide regimens in central precocious puberty". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 91 (5): 1862–7. doi:10.1210/jc.2005-1500. PMID 16449344.
- ↑ Saleh F, Niel T, Fishman M (2004). "Treatment of paraphilia in young adults with leuprolide acetate: a preliminary case report series". J Forensic Sci. 49 (6): 1343–8. doi:10.1520/JFS2003035. PMID 15568711.
- ↑ Schober JM, Byrne PM, Kuhn PJ (2006). "Leuprolide acetate is a familiar drug that may modify sex-offender behaviour: the urologist's role.". BJU international. 97 (4): 684–6. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2006.05975.x. PMID 16536753.
- ↑ Schober JM, Kuhn PJ, Kovacs PG, Earle JH, Byrne PM, Fries RA (2005). "Leuprolide acetate suppresses pedophilic urges and arousability.". Archives of Sexual Behavior. 34 (6): 691–705. doi:10.1007/s10508-005-7929-2. PMID 16362253.
- ↑ Doraiswamy PM, Xiong GL (2006). "Pharmacological strategies for the prevention of Alzheimer's disease". Expert Opin Pharmacother. 7 (1): 1–10. doi:10.1517/14656566.7.1.1. PMID 16370917.
- ↑ David A. Wolfe; Eric J. Mash (9 October 2008). Behavioral and Emotional Disorders in Adolescents: Nature, Assessment, and Treatment. Guilford Press. pp. 556–. ISBN 978-1-60623-115-9. Retrieved 24 March 2012.
- ↑ http://www.rxlist.com/lupron-side-effects-drug-center.htm
- ↑ Mutschler, Ernst; Schäfer-Korting, Monika (2001). Arzneimittelwirkungen (in German) (8 ed.). Stuttgart: Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft. pp. 372–3. ISBN 3-8047-1763-2.
- ↑ Wuttke, W; Jarry, H; Feleder, C; Moguilevsky, J; Leonhardt, S; Seong, J. Y.; Kim, K (1996). "The neurochemistry of the GnRH pulse generator". Acta neurobiologiae experimentalis. 56 (3): 707–13. PMID 8917899.
- ↑ Geier M, Geier D (2005). "The potential importance of steroids in the treatment of autistic spectrum disorders and other disorders involving mercury toxicity". Med Hypotheses. 64 (5): 946–54. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2004.11.018. PMID 15780490.
- ↑ Allen A (2007-05-28). "Thiomersal on trial: the theory that vaccines cause autism goes to court". Slate. Retrieved 2008-01-30.
- ↑ "Testosterone regulation". Research Autism. 2007-05-07. Retrieved 2015-04-09.
- 1 2 "Maryland medical board upholds autism doctor's suspension". Chicago Tribune. May 11, 2011.
- ↑ "John and Jane Doe v. Ortho-Clinical Diagnostics, Inc", US District Court for the Middle District of North Carolina, July 6, 2006
- ↑ "Dr. Mark Geier Severely Criticized", Stephen Barrett, M.D., Casewatch.org
- ↑ Mills S, Jones T (2009-05-21). "Physician team's crusade shows cracks". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved 2009-05-21.
- ↑ 'Miracle drug' called junk science: Powerful castration drug pushed for autistic children, but medical experts denounce unproven claims, Chicago Tribune, May 21, 2009
- ↑ Desmarchelier M, Lair S, Dunn M, Langlois I.Primary hyperaldosteronism in a domestic ferret with an adrenocortical adenoma. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2008 Oct 15;233(8):1297-301.PMID 19180717
- ↑ Boari A, Papa V, Di Silverio F, Aste G, Olivero D, Rocconi F. Type 1 diabetes mellitus and hyperadrenocorticism in a ferret. Vet Res Commun. 2010 Jun;34 Suppl 1:S107-10. doi: 10.1007/s11259-010-9369-2.PMID 20446034.
- ↑ https://nwhn.org/lupron®-–-what-does-it-do-women’s-health
External links
- Lupron Injection (package insert from abbott)
- Reforming (purportedly) Non-Punitive Responses to Sexual Offending (journal article discussing use of Lupron as a form of reforming sex offender law)
- Lupron victims hub, website against use of this drug.