Photon diffusion equation
Photon diffusion equation is a second order partial differential equation describing the time behavior of photon fluence rate distribution in a low-absorption high-scattering medium.
Its mathematical form is as follows.
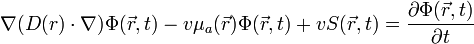 where
where 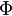 is photon fluence rate (W/cm2),
is photon fluence rate (W/cm2), 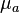 is absorption coefficient (cm−1),
is absorption coefficient (cm−1), 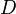 is diffusion constant,
is diffusion constant, 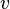 is the speed of light in the medium (m/s), and
is the speed of light in the medium (m/s), and 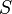 is an isotropic source term (W/cm3).
is an isotropic source term (W/cm3).
Its main difference with diffusion equation in physics is that photon diffusion equation has an absorption term in it.
Application
Medical Imaging
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/16/2013. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.