RWD 1
| RWD-1 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | Sports plane |
| National origin | Poland |
| Manufacturer | Warsaw University of Technology workshops |
| Designer | RWD team |
| First flight | September 1928 |
| Introduction | 1928 |
| Retired | 1930 |
| Primary user | Poland |
| Number built | 1 |
|
| |
The RWD-1 was a Polish sports plane of 1928, a single-engine high-wing monoplane constructed by the RWD design team.
Development
The RWD-1 was the first aircraft constructed by the RWD team of Stanisław Rogalski, Stanisław Wigura and Jerzy Drzewiecki in the Aviation Section of Mechanic Students' Club of Warsaw University of Technology. It was designed in late 1927. The plane was built with a financial help of the LOPP organization. One prototype was built for static trials, and one flying prototype (registration SP-ACC), completed and flown by the designer Jerzy Drzewiecki in September 1928.
Its unusual feature was a unique, fish-shaped fuselage, similar to early Messerschmitt's designs (M17). Two crewmen sat in tandem inside the fuselage and had only side openings in its upper part. In front of the pilot's head there was an upper part of the fuselage, supporting wings, limiting his view forward, though its profile was thin. This shape was repeated in following RWD designs. The aircraft was evaluated as a quite good design, with an original construction. It had high glide ratio of 12, and its payload was bigger than its empty weight. It was not built in any quantities, but gave a basis to further more successful RWD designs: RWD-2, RWD-3, RWD-4, RWD-7, and, partly RWD-5.
The prototype took part in the 2nd Polish Light Aircraft Contest in 1928, but did not complete it due to engine breakdown. In 1929 it undertook a raid around Poland. It was scrapped in winter of 1929/1930.
Description
Wooden construction single-engine high-wing cantilever monoplane, conventional in layout. The fuselage rectangular in cross-section, narrowing in upper part, plywood covered. Single-spar one-part trapezoid wings, covered with canvas and plywood in front. Cantilever empennage, covered with plywood (stabilizers) and canvas (rudder and elevators). The crew of two sat in tandem. The crew cockpits were open on the sides in upper part, and had individual doors (first cockpit - on the right, second one - on the left). A 2-cylinder air-cooled 40 hp ABC Scorpion II boxer engine (34 hp nominal power) was in front, driving two-blade wooden propeller Szomański (1,5 m diameter). Conventional fixed landing gear, sprung with a rubber rope, with a rear skid. Fuel tank in fuselage front (fuel consumption 9 l/h).
Specifications (RWD-1)
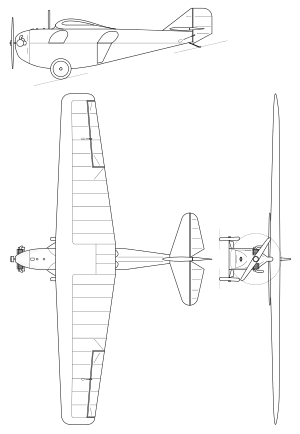
Data from Glass, A. (1977)
General characteristics
- Crew: One, pilot
- Capacity: One, passenger / second pilot
- Length: 6 m (19 ft 8 in)
- Wingspan: 9.8 m (32 ft 2 in)
- Height: 1.7 m (5 ft 7 in)
- Wing area: 13.6 m² (146.3 ft²)
- Empty weight: 206 kg (453 lb)
- Useful load: 211 kg ()
- Loaded weight: 417 kg (918 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × ABC Scorpion II 2-cylinder air-cooled flat engine, 40 hp (53.6 kW)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 135 km/h (84 mph/h)
- Cruise speed: 115 km/h
- Stall speed: 65 km/h ()
- Range: 500 km (310 mi)
- Service ceiling: 1,950 m (6,396 ft)
- Rate of climb: 1.8 m/s, 108 m/min (354 ft/min)
- Wing loading: 30.5 kg/m² (6.3 lb/ft²)
- Take-off run: 100 m
- Landing run: 130 m
See also
- Related development
- Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
References
- Andrzej Glass: "Polskie konstrukcje lotnicze 1893-1939" (Polish aviation constructions 1893-1939), WKiŁ, Warsaw 1977 (Polish language, no ISBN)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to RWD-1. |