Bombesin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
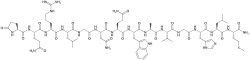
Pyr-Gln-Arg-Leu-Gly-Asn-Gln-Trp-Ala-Val-Gly-His-Leu-Met-NH2 | |
| Identifiers | |
| 31362-50-2 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL437027 |
| ChemSpider | 17290379 |
| 616 | |
| PubChem | 16133800 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C71H110N24O18S | |
| Molar mass | 1619.85 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Bombesin is a 14-amino acid peptide[1] originally isolated from the skin of the European fire-bellied toad (Bombina bombina).[2] It has two known homologs in mammals called neuromedin B and gastrin-releasing peptide. It stimulates gastrin release from G cells. It activates three different G-protein-coupled receptors known as BBR1, -2, and -3.[3] It also activates these receptors in the brain. Together with cholecystokinin, it is the second major source of negative feedback signals that stop eating behaviour.[4]
Bombesin is also a tumor marker for small cell carcinoma of lung, gastric cancer, pancreatic cancer, and neuroblastoma.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ Gonzalez N, Moody TW, Igarashi H, Ito T, Jensen RT (February 2008). "Bombesin-related peptides and their receptors: recent advances in their role in physiology and disease states". Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes and Obesity. 15 (1): 58–64. doi:10.1097/MED.0b013e3282f3709b. PMC 2631407
 . PMID 18185064.
. PMID 18185064. - ↑ "Isolation and Structure of Bombesin and Alytesin, two Analogous Active Peptides from the Skin of the European Amphibians Bombina and Alytes" by A. ANASTASI, V. ERSPAMER and M. BuccI http://download.springer.com/static/pdf/258/art%253A10.1007%252FBF02145873.pdf?auth66=1384653010_1b792225201410812f5c123e46ce10a5&ext=.pdf[]
- ↑ Weber HC (February 2009). "Regulation and signaling of human bombesin receptors and their biological effects". Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes and Obesity. 16 (1): 66–71. doi:10.1097/med.0b013e32831cf5aa. PMID 19115523.
- ↑ Yamada K, Wada E, Wada K (November 2000). "Bombesin-like peptides: studies on food intake and social behaviour with receptor knock-out mice". Annals of Medicine. 32 (8): 519–29. doi:10.3109/07853890008998831. PMID 11127929.
- ↑ Ohlsson B, Fredäng N, Axelson J (December 1999). "The effect of bombesin, cholecystokinin, gastrin, and their antagonists on proliferation of pancreatic cancer cell lines". Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology. 34 (12): 1224–9. doi:10.1080/003655299750024742. PMID 10636070.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/6/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.