Singapore–South Africa relations
 |
|
Singapore |
South Africa |
|---|---|
Singapore–South Africa relations refer to the bilateral relations between the Republic of Singapore and the Republic of South Africa. The connections between the two countries are mainly based on the Commonwealth of Nations, which is their common bond, and the interactions in trading, sight-seeing and trading aspects. Both countries cooperate in social and economic development issues.[1]
Singapore has a High Commission in Pretoria while South Africa has a High Commission in Singapore.
History
On August 9, 1965, Singapore was expelled from Malaysia and became an independent state. However, due to the apartheid policy, it did not establish diplomatic relations with South Africa until 1992, when the two countries signed agreements to do so.[2] In 1994, South Africa joined the Commonwealth, resulting in the Embassies of both countries being renamed High Commissions and the Ambassadors becoming High Commissioners.
On March 5, 1997, Nelson Mandela became the first President of South Africa to visit Singapore, where he met President Ong Teng Cheong and Senior Minister Lee Kuan Yew.[3] In 2007, S.R. Nathan became the first President of Singapore to visit South Africa.[4]
In January 2013, International Enterprise Singapore set up a centre in Johannesburg, its first overseas centre in Sub-Saharan Africa.[5]
Trade relations
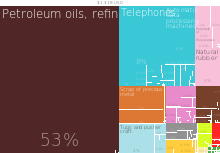
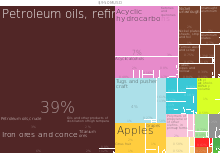
In 2011, the total trade value between Singapore and South Africa was worth S$2.54 billion (or R16 billion).[4] In 2012, the export value from Singapore to South Africa was worth US$1.31 billion, [6] The export value from South Africa to Singapore was worth US$950 million.[6]
Singapore exports were mainly communication equipment, electrical machines, office and data machines, manufactured articles, general industrial machines, plastics, crude rubber, textiles, coffee and spices to South Africa.
During the same period, South Africa mainly exported organic chemicals, petroleum and its products, iron and steels, non-ferrous metals, metal manufactures, vegetables, inorganic chemicals, metallic ores and scraps and paper manufactures to Singapore.[2]
In 2011, the direct investment value from Singapore to South Africa was worth S$491 million (or R3.23 billion),[4] while the direct investment value from South Africa to Singapore was worth 19.04 million Singapore dollars (or R125 million).[4]
Singapore Airlines operates a flight between Singapore Changi Airport and Cape Town International Airport in South Africa, via O.R. Tambo International Airport in Johannesburg.[7] During the 1990s, South African Airways also operated direct flights to Singapore.[8] It later established a codeshare with Singapore Airlines on daily flights between Singapore and Johannesburg.[9]
See also
References
- ↑ Srimal Fernando. South Africa and Singapore partnership continues to grow stronger. The Diplomacy Society. [2015-04-12].
- 1 2 Singapore (Republic of). Department of International Relations and Cooperation, Republic of South Africa. Department of International Relations and Cooperation, Republic of South Africa. [2015-04-10].
- ↑ SINGAPORE: SOUTH AFRICA'S PRESIDENT NELSON MANDELA VISIT. The Associated Press. 1997-03-05 [2015-04-10].
- 1 2 3 4 Bilateral Relations Department of International Relations and Cooperation [2015-04-11].
- ↑ "Africa". Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Singapore. Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Singapore. Retrieved 2015-04-10.
- 1 2 What did Singapore export to South Africa in 2012?. Center for International Development of Harvard University. Center for International Development of Harvard University. [2015-04-10].
- ↑ Where we fly. Singapore Airlines. Singapore Airlines. [2015-04-11].
- ↑ Encyclopedia of African Airlines, Ben R. Guttery, McFarland & Company, 1998, page 192
- ↑ SAA customers can now fly to Singapore, South African Airways, 31 August 2006
.svg.png)