Sulfaquinoxaline
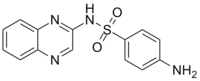 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4-Amino-N-2-quinoxalinylbenzenesulfonamide | |
| Other names
4-Amino-N-2-quinoxalinylbenzenesulfonamide | |
| Identifiers | |
| 59-40-5 | |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL1437847 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.385 |
| UNII | WNW8115TM9 |
| Properties | |
| C14H12N4O2S | |
| Molar mass | 300.366 g/mol |
| Melting point | 247.5 °C (477.5 °F; 520.6 K) |
| slightly soluble in water | |
| Solubility | slightly soluble in ethanol, acetone, soluble in aqueous alkaline solutions |
| Pharmacology | |
| QP51AG03 (WHO) | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Sulfaquinoxaline (IUPAC name: 4-Amino-N-2-quinoxalinylbenzenesulfonamide) is a veterinary medicine which can be given to cattle and sheep to treat coccidiosis.It is available in Pakistan with Sanna Laboratories in combination with Amprolium and Vitamin K as potential treatment of coccidiosis[2]
References
- ↑ Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, pp. 3–26, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
- ↑ Philip H. Howard, ed. (2003), Georgis' Parasitology for Veterinarians, 5, Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, p. 98, ISBN 0-87371-976-X, retrieved 2009-12-03
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/1/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.