Witley
| Witley | |
 Witley railway station in the Wormley locality of Witley Parish |
|
 Typical Houses of Petworth Road, Witley |
|
 Witley |
|
| Area | 27.76 km2 (10.72 sq mi) |
|---|---|
| Population | 8,130 (Civil Parish 2011)[1] |
| – density | 293/km2 (760/sq mi) |
| OS grid reference | SU947398 |
| – London | 33.5 miles (53.9 km) |
| Civil parish | Witley |
| District | Waverley |
| Shire county | Surrey |
| Region | South East |
| Country | England |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | Godalming |
| Postcode district | GU8 |
| Dialling code | 01428 |
| Police | Surrey |
| Fire | Surrey |
| Ambulance | South East Coast |
| EU Parliament | South East England |
| UK Parliament | South West Surrey |
Coordinates: 51°09′00″N 0°38′46″W / 51.150°N 0.646°W
Witley is a village and civil parish in the Borough of Waverley in Surrey, England centred 2.6 miles (4 km) south west of the town of Godalming and 6.6 miles (11 km) southwest of the county town, Guildford. The land is made up of mixed rural (from woods to cultivated fields, including some of the forested Greensand Ridge) and suburban areas.
As a civil parish it is unusual in that it includes the small town of Milford in the north. Occupying its hills in the south-west are Sandhills and Brook.
Witley Common is a wide National Trust expanse crossed by the A3 road. The village is served by two stations on the Portsmouth Direct Line: Witley station, actually sited to the south in nearby Wormley, and, to the north, Milford station, which is more or less equidistant between Milford and Witley. Its church dates to the pre-Norman Conquest period of the Kingdom of England and the village has a private sector, charitable co-educational boarding and day school founded in 1553 by King Edward VI and Nicholas Ridley.
History
Much of the history is described by way of its historical sites below.
Witley appears in the Domesday Book of 1086 as Witlei. Its domesday assets were held by Gislebert (Gilbert), son of Richere de L'Aigle. It rendered: 12 hides; 1 church, 15 ploughs, 3 acres (1.2 ha) of meadow, woodland worth 30 hogs, in the Godalming Hundred and rendered £16.[2]
In 1848, Samuel Lewis's "topographical dictionary of England" describes Witley as
A parish, in the union of Hambledon ... containing 1488 inhabitants ... situated on the road from Godalming to Petworth, and comprises 6,324 acres (2,559 ha), of which 3,150 acres (1,270 ha) are arable, 900 acres (360 ha) pasture, 1,100 acres (4.5 km2) wood, and 1,174 acres (4.75 km2) waste (infertile land). A pleasure-fair is held on 23 April. The living is a discharged vicarage[n 1], with that of Thursley annexed, valued in the king's books at £17. 15. 10.; patron and incumbent, the Rev. J. Chandler; the great tithes of Witley have been commuted for £13, and the small for £200. The church is a cruciform structure, principally in the early English style, with a central tower surmounted by a spire, and contains monuments to the Chandler and Webb families, and some ancient brasses. A district church, dedicated to St. John the Evangelist, was built at Milford in 1836: the living is in the gift of the Brodrick family. There is a place of worship for Calvinists.
In 1911 historian and factfinder for the Victoria County Histories that turned to Surrey that year, H.E. Malden, excluding many words about the advowson, of no general notability given their general forfeiture in favour of church-appointed clergy, wrote 1,857 words about the church history with a layout plan.[3] As to manors which owned virtually all of the land in the medieval period, seven existed of which three were senior as had nobility living in them or owning them whereas the others did not; Malden wrote 3,788 words, mostly of their ownership and manor houses.[3] These senior manors are summarised below whereas the other four were Wytley Chesberies or Wytley Cheasburies Manor, Mousehill Manor, Rake Manor and Roke or Roakeland Manor.[3]
Witley Manor
Earl Godwin (father of Harold Godwinson) is the first known lord of the manor. One of William the Conqueror's knights Engenulf de Aquila's grandson held this land in 1086, Gilbert de Aquila. Then Richer de Aquila forfeited his land to the crown for complicity in the rebellion of William Clito against the crown. Malden reveals the legal term then used, one still used today, escheat.
William de Warenne, 5th Earl of Surrey, Gilbert's nephew by marriage, was granted it, who died in 1240.[4] However, this was to no effect, as he gave it back. It reverted to the King, who then granted it to Peter de Rivaulx, who similarly suffered a deprivation in 1234. In 1246 Gilbert Marshal, 4th Earl of Pembroke was awarded it, and surrendered it; then still termed part of the honour of Aquila, Peter of Savoy and later Earl of Richmond, uncle of Queen Eleanor, received this land; homage stopped, rents rose and, on the baronial victory in 1264, Peter of Savoy having fled from the country, this manor was briefly in the custody of Gilbert de Clare, 6th Earl of Hertford and Earl of Gloucester. After his success at Evesham in 1264, Eleanor was seized, who granted the tenants a release from the oppressive exactions of her predecessor on condition that they should cause a yearly service to be held in Witley Church for the souls of her husband and of Peter of Savoy.[3]
Queen Isabella, Queen to Edward II, surrendered it with her other lands in 1330 and it formed part of next Queen Philippa of Hainault's dower in January 1330–31. After an intriguing further incidence of exhortation[n 2], many years later Sir Bryan Stapilton held it for life, followed by James Fiennes, 1st Baron Saye and Sele, soldier and politician. He was put to death during the Kentish rebellion of Jack Cade, and the Manor passed to the King's brother Jasper Tudor (created Duke of Bedford, Earl of Pembroke); when the Wars of the Roses raged the Earl of Kent was awarded it, followed by the soon-to-be executed George Plantagenet, 1st Duke of Clarence. Then we see still more royal holding, with stewards Sir George Brown, Sir William Fitz William, Sir Anthony Browne and Henry VIII's server of the chamber, Thomas Jones. In 1551 new Baron Saye and Sele (dubious, per Malden) Edward Clinton, 1st Earl of Lincoln sold the estate to Richard Sackville (escheator) for Surrey, who made William More of Loseley steward. Elizabeth I had it within her powers by the time of her accession to just grant the manor, possibly due to the internal wars of religion and Sir Francis Wolley (see his daughter Hannah Woolley), to Sir George More in 1605. He subsequently sold the park to Sir Edward More, and the title of the Manor to Henry Bell of Rake Manor. After this time the Manor was never again held by the nobility.
Lea Park known as Witley Park
The early history of Lea Park (renamed Witley Park during the 20th century) is entwined with that of Witley Manor. Specific frequent appointments to the office of keeper occur in the Patent Rolls, sometimes in conjunction with that of Ashurst Park: in 1514, for example, to Thomas Jones and also to his son.[3] In 1656 Edward More, grandson of Sir Edward, sold it to Thomas Russell; it was probably already broken up into farms, and James Cecil, 4th Earl of Salisbury had half of it via marriage. By heirs expiring of the other moiety, James Cecil, 6th Earl of Salisbury received the remaining (as some is thought to have been sold off) whole of Lea park in 1730. His son sold it to a William Smith of Godalming in 1791. Allen Chandler sold it to the Earl of Derby in 1876.[3] It was subsequently sold to Whitaker Wright (see below) for £250,000.[5]
Oxenford Grange

This was within Peper Harow Park, but in the parish of Witley, and was early held by Richer de Aquila and subsequently his grandson heir Gilbert. It was included in the Dissolution of the Monasteries grant of Waverley Abbey to Sir William Fitz William, with which it descended to Anthony Browne, 1st Viscount Montagu who died seised of a messuage called Oxenford, 9 October 1592. Similarly to the above, Sir George More of Loseley in 1609, Oxenford passed to Bartholomew Hone and heir John Chesterton of St. Giles in the Fields in 1619. In 1667 Antony Covert and his son conveyed their third to John Platt of Westbrook and his heirs; his son Sir John Platt and a John Smith sold it to prominent parliamentarian Denzil Holles, 1st Baron Holles; the other third was sold by the Fox family to George Brodrick, 4th Viscount Midleton c. 1822; his son employed Augustus Welby Northmore Pugin to build an imitation 13th century farm here.[3]
Landmarks
_-_geograph.org.uk_-_1543211.jpg)
- All Saints' Church is built from surviving Anglo-Saxon England stonework and later Norman architecture, demonstrating that the village has existed since at least Saxon times. The church building was transformed by the Normans and enlarged into a cruciform shape towards the end of the 12th century, when its tower was also erected. The church contains an inscribed stone, set in the chancel wall, bearing the name of the Duke of Clarence (see below), which is believed to be part of an unfinished memorial to one of his bailiffs.[6][7] The church is Grade I listed (the top category of listing).[8]
- Witley Park, the home of Whitaker Wright, was built in the 1890s at a cost of £1.85 million. It was one of the most lavish private residences in the world. The grounds included a series of three interconnecting lakes and an underwater billiard room. The main building burnt to the ground in 1953. Today the grounds and remaining buildings are private family homes.
- Old Cottage and Step Cottage, dating from the 15th and 16th centuries, are close to the church.
- White Hart, the village public house, is mostly Elizabethan and is said to stand on the site of a Saxon inn.
Semaphore/Telegraph Station
On Bannicle or Bannack Hill there was an Admiralty telegraph station which was built in 1822 as part of a semaphore line between the Admiralty in London and Portsmouth. It was about 30 yards east of Hill House,51°08′11″N 0°39′32″W / 51.1365°N 0.6588°W but no trace of the station remains.[9] William Cobbett in Rural Rides referred to the station when travelling through the hills of Hambledon. "On one of these hills is one of those precious jobs, called semaphores. For what reason this pretty name is given to a sort of Telegraph house, stuck up at public expense upon a high hill; for what reason this outlandish name is given to the thing, I must leave the reader to guess; but as to the thing itself; I know that it means this; a pretence for giving a good sum of public away every year ..."[10]
| Next station upwards | Admiralty Semaphore line 1822 | Next station downwards |
| Pewley Hill | Bannicle Hill | Haste Hill |
Geography

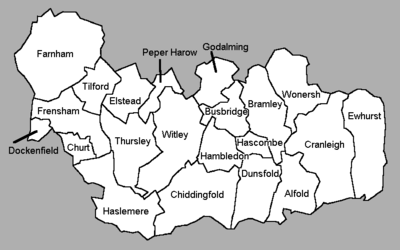
Witley is a village and civil parish in the Borough of Waverley in Surrey 2.6 miles (4 km) south west of Godalming and 6.6 miles (11 km) southwest of the county town, Guildford. The village lies just east of the A3 from London to Portsmouth between Guildford and Petersfield; London is 33.5 miles (53.9 km) northeast as the crow flies.[11]
Witley Civil Parish contains the large village of Milford (arguably a small town to the north, which also has the next railway station on the line to London, however, which is closer to Wheelerstreet and Witley historic village along than to Milford)[n 3] and the localities set out in this article, all of which, apart from Culmer, Wormley, Sandhills and Brook are contiguous, linked by unbroken paved roads and development forming a wide arc surrounded by Witley Common or by the Witley Stream, Enton lakes and ponds.[12] The census area Waverley Middle Layer Super Output Area 12 (which excludes Milford but adds most of Hambledon, Thursley and Hascombe) gives a population of 6,619 in 2001, whereas the civil parish had a population of 7,703.[13] If the population of Thursley CP (654) is subtracted and those of Hascombe (241) and Hambledon CPs (765) from Area 12, Witley's population, excluding the major settlement of Milford is 4,959.
Witley civil parish council consists of 16 unpaid councillors who run a website with sections for Witley and Milford; as with all civil parishes, and Waverley is entirely parished, charging a small annual precept on council tax.[14] Among their tasks are the management of Witley Recreation Ground, 43 allotments, upkeep of village halls and organisation of annual community events.
Witley Common
Witley Common, which belongs to the National Trust, directly adjoins many localities of the village.[15]
Localities
The first five are named and form a loose cluster, though some smallholdings and playing fields buffer them: Cramhurst, Wheelerstreet, Crossways, Witley (historic centre) and Culmer.
Also in the parish are Sandhills, Brook and most of Wormley.
Education
- Witley Infants School, opposite the church, is a fine example of a 19th-century school constructed in 1836, one year before Queen Victoria was crowned.
- King Edward's School is a private school due south of the village centre.
Transport
- The village is served by Witley railway station, although those living in the northern part of the village are closer to Milford station. Both stations are located on the Portsmouth Direct Line railway.
Notable people
- Lionel of Antwerp, Duke of Clarence (1338–1368), brother of Edward IV, was lord of the manor of Witley. Other owners included Godwin, Earl of Wessex, father of King Harold; Peter of Savoy; and Edward I's wife, Queen Margaret, who commissioned oak from the village to make shingles for the roof of the King's Hall at Westminster.
- David Lloyd George (1863–1945), prime minister, had a house Timbers, which he would visit whenever he needed to escape from the stress of high office.
- Terry Scott (1927–1994), comedian who starred in the BBC domestic sitcom Terry and June with June Whitfield, lived in the village.
- Myles Birket Foster (1825–1899), artist, is buried in the churchyard.
- Whitaker Wright (1846–1904), mining entrepreneur, was found guilty of fraud at the Royal Courts of Justice and committed suicide shortly afterwards. He is buried in the churchyard beneath an imposing marble slab.
- George Eliot (1819–1880), English novelist, spent her final years in the village.
- Gertrude Mary Tuckwell (1861–1951), trade unionist, social reformer and author, lived the last years of her life in Little Woodlands, Combe Lane.
- James John Joicey (1871–1932), amateur entomologist and owner of the Hill Museum.
- Frederick Williamson (1835–1900), visual artist known for his paintings of landscapes featuring sheep, is buried in the churchyard.
- Tony Banks (born 27 March 1950 in East Hoathly, Sussex, England), founding member and keyboardist of the progressive rock group Genesis.
Demography and housing
| Output area | Detached | Semi-detached | Terraced | Flats and apartments | Caravans/temporary/mobile homes | shared between households[1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Civil Parish; includes town of Milford in the north) | 1,187 | 982 | 491 | 501 | 10 | 2 |
The average level of accommodation in the region composed of detached houses was 28%, the average that was apartments was 22.6%.
| Output area | Population | Households | % Owned outright | % Owned with a loan | hectares[1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Civil Parish) | 8,130 | 3,173 | 36.2% | 36.7% | 2,776 |
The proportion of households in the civil parish who owned their home outright compares to the regional average of 35.1%. The proportion who owned their home with a loan compares to the regional average of 32.5%. The remaining % is made up of rented dwellings (plus a negligible % of households living rent-free).
See also
Notes and references
- Notes
- ↑ The living of Aston Cantlow was of the same form; holders of land that was the glebe when it converted from a rectory may be liable for chancel repair liability if claimed by the church; they were in 1848 the impropriators listed by Lewis.
- ↑ See the original source for more details
- ↑ Milford Station has direct access from Wheelerstreet along Rake Lane and from Witley along a straight track behind the school and beside the railway
- References
- 1 2 3 Key Statistics; Quick Statistics: Population Density United Kingdom Census 2011 Office for National Statistics Retrieved 21 November 2013
- ↑ Surrey Domesday Book
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 H.E. Malden (editor) (1911). "Parishes: Witley". A History of the County of Surrey: Volume 3. Institute of Historical Research. Retrieved 10 November 2012.
- ↑ Morris, Marc, The Bigod Earls of Norfolk in the thirteenth century, (The Boydell Press, 2005), 31.
- ↑ "The swindler, the cyanide pill and the underwater ballroom: The story behind Britain's most bizarre folly". 8 November 2011. Retrieved 24 January 2016.
- ↑ All Saints (Church of England community website)
- ↑ The Church of England – All Saints Church, Witley
- ↑ All Saints, Witley – Grade I – Historic England. "Details from listed building database (1260732)". National Heritage List for England. Retrieved 8 December 2013.
- ↑ Historic Environment RecordHER 3504 – Admiralty Telegraph Station circa 1822 (Site of)
- ↑ William Cobbett Rural Rides Penguin English Library 1967
- ↑ Grid reference Finder measurement tools
- ↑ Ordnance Survey map, courtesy of English Heritage
- ↑ UK Census search by Waverley Middle Layer Super Output Area 12 and by Parish
- ↑ Witley Parish Council
- ↑ National Trust
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Witley. |
