Parlement
A parlement (French pronunciation: [paʁləmɑ̃]) was a provincial appellate court in the France of the Ancien Régime, i.e. before the French Revolution. In 1789 13 parlements existed, the most important of which was by far the Parlement of Paris. While English word parliament derives from this French term, parlements were not legislative bodies. They consisted of a dozen or more appellate judges, or about 1,100 judges nationwide. They were the court of final appeal of the judicial system, and typically wielded much power over a wide range of subject matter, particularly taxation. Laws and edicts issued by the Crown were not official in their respective jurisdictions until the parlements gave their assent by publishing them. The members were aristocrats called nobles of the gown who had bought or inherited their offices, and were independent of the King.
From 1770 to 1774 the Lord Chancellor, Maupeou, tried to abolish the Parlement of Paris in order to strengthen the Crown; however, when King Louis XV died in 1774, the parlements were reinstated. The parlements spearheaded the aristocracy's resistance to the absolutism and centralization of the Crown, but they worked primarily for the benefit of their own class, the French nobility. Alfred Cobban argues that the parlements were the chief obstacles to any reform before the Revolution, as well as the most formidable enemies of the French Crown. He concludes that the
"Parlement of Paris, though no more in fact than a small, selfish, proud and venal oligarchy, regarded itself, and was regarded by public opinion, as the guardian of the constitutional liberties of France."[1]
In November 1789, early in the French Revolution, all parlements were suspended, and they were formally abolished in September 1790.[2]
 |
| Kingdom of France |
|---|
| Structure |
History
The political institutions of the Parlement in Ancien Régime France developed out of the King's Council (Fr. Conseil du roi, Lat. curia regis), and consequently enjoyed ancient, customary consultative and deliberative prerogatives.[3] In the 13th century, the parlements acquired judicial functions, then the droit de remontrance against the king. The parlement judges were of the opinion that their role included active participation in the legislative process, which brought them into increasing conflict with the ever increasing monarchical absolutism of the Ancien Régime, as the lit de justice evolved during the 16th century from a constitutional forum to a royal weapon, used to force registration of edicts.[4]

Originally, since c. 1250, there was only the Parlement of Paris, severed from the King's Council in 1307, with sessions held inside the medieval royal palace on the Île de la Cité, still the site of the Paris Hall of Justice. The Paris parlement's jurisdiction covered the entire kingdom as it was in the 14th century, but did not automatically advance in step with the Crown's ever expanding realm. In 1443, following the turmoil of the Hundred Years' War, King Charles VII of France granted Languedoc its own parlement by establishing the Parlement of Toulouse, the first parlement outside Paris; its jurisdiction extended over most of southern France.
Fronde
The Parlement of Paris played a major role in stimulating the nobility to resist the expansion of royal power by military force in the Fronde, 1643-1652. In the end, the King won out and the nobility was humiliated.[5]
Louis XIV
The parlements could withhold their assent by formulating remonstrances against the king's edicts, forcing the king to react, sometimes resulting in repeated resistance by the parlements, which the king could only terminate in his favour by issuing a Lettre de jussion, and, in case of continued resistance, appearing in person in the parlement: the Lit de justice. In such a case, the parlement's powers were be suspended for the duration of this royal session. King Louis XIV moved to centralize authority into his own hands, imposing certain restrictions on the parlements. In 1665, he ordained that a Lit de justice could be held without the king having to appear in person. In 1667, he limited the number of remonstrances to only one. In 1671–1673, however, the parlements resisted the taxes occasioned by the Dutch War. In 1673, the king imposed additional restrictions that stripped the parlements of any influence upon new laws by ordaining that remonstrances could only be issued after registration of the edicts. After Louis' death in 1715, all the restrictions were discontinued by the regent, although some of the judges of the Parlement of Paris accepted royal bribes to restrain that body until the 1750s.[6]
Provinces
From 1443 until the French Revolution, several other parlements were steadily created all over France, until at the end of the Ancien Régime there were provincial parlements in: (clockwise from the north) Douai, Arras, Metz, Nancy, Colmar, Dijon, Besançon, Grenoble, Aix, Perpignan, Toulouse, Pau, Bordeaux, Rennes, and Rouen. These locations were provincial capitals of those provinces with strong historical traditions of independence before they were annexed to France. Assembled in the parlements, the largely hereditary members, the provincial nobles of the gown were the strongest decentralizing force in a France that was more multifarious in its legal systems, taxation, and custom than it might have seemed under the apparent unifying rule of its kings. Nevertheless, the Parlement of Paris had the largest jurisdiction of all the parlements, covering the major part of northern and central France, and was simply known as "the Parlement".
In some regions provincial States-General also continued to meet and legislate with a measure of self-governance and control over taxation within their jurisdiction.
All the parlements could issue regulatory decrees for the application of royal edicts or of customary practices; they could also refuse to register laws that they adjudged as either untimely or contrary to the local customary law (and there were 300 customary law jurisdictions). Tenure on the court was generally bought from the royal authority; and such positions could be made hereditary by payment of a tax to the King called la Paulette.
Provincial parlements
| Provincial "parlements" or "conseils souverains" (shown in historic provinces of France) during the Ancien Régime. Dates indicate creation of the parlement.[7] | ||
|---|---|---|
|
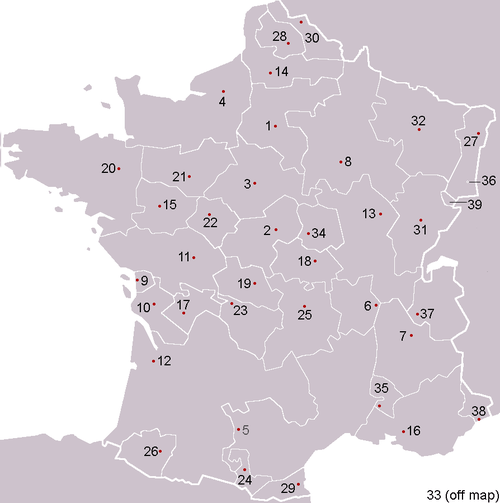 | |
Role leading to French Revolution
After 1715, during the reigns of King Louis XV of France and King Louis XVI, the parlements repeatedly challenged the crown for control over policy, especially regarding taxes and religion.[8] The Parlement had the duty to record all royal edicts and laws. Some, especially the Parlement of Paris, gradually acquired the habit of refusing to register legislation with which they disagreed until the king held a lit de justice or sent a lettre de jussion to force them to act. Furthermore, the parlements could pass arrêts de réglement, which were laws that applied within their jurisdiction. In the years immediately before the start of the French Revolution in 1789, their extreme concern to preserve Ancien Régime institutions of noble privilege prevented France from carrying out many simple reforms, especially in the area of taxation, even when those reforms had the support of the king.[9]
Chancellor René Nicolas de Maupeou sought to reassert royal power by suppressing the parlements in 1770. A furious battle resulted and after King Louis XV died, the parlements were restored.[10]
The beginning of the proposed radical changes began with the Protests of the Parlement of Paris addressed to Louis XVI in March 1776, in which the Second Estate, the nobility, resisted the beginning of certain reforms that would remove their privileges, notably their exemption from taxes. The objections made to the Parlement of Paris were in reaction to the essay, Réflexions sur la formation et la distribution des richesses ("Reflections on the Formation and Distribution of Wealth") by Anne-Robert-Jacques Turgot. The Second Estate reacted to the essay with anger to convince the king that the nobility still served a very important role and still deserved the same privileges of tax exemption as well as for the preservation of the guilds and corporations put in place to restrict trade, both of which were eliminated in the reforms proposed by Turgot.[11]
In their Remonstrance against the Edict suppressing the Corvée (March 1776), the Parlement of Paris - afraid that a new tax would replace the Corvée, and that this tax would apply to all, introducing equality as a principle - dared to remind the king:
- The personal service of the clergy is to fulfill all the functions relating to education and religious observances and to contribute to the relief of the unfortunate through its alms. The noble dedicates his blood to the defense of the state and assists to sovereign with his counsel. The last class of the nation, which cannot render such distinguished service to the state, fulfills its obligation through taxes, industry, and physical labor.[12]
The Second Estate (the nobility) consisted of approximately 1.5% of France's population, and was exempt from almost all taxes, including the Corvée Royale, which was a recent mandatory service in which the roads would be repaired and built by those subject to the corvée. In practice, anyone who paid a small fee could escape the corvee, so this burden of labor fell only to the poorest in France. The Second Estate was also exempt from the Gabelle, which was the unpopular tax on salt, and also the Taille, the oldest form of taxation in France.[13]
The Second Estate feared they would have to pay the tax replacing the suppressed Corvée. The nobles saw this tax as especially humiliating and below them, as they took great pride in their titles and their lineage, many of whom had died in defense of France. They saw this elimination of tax privilege as the gateway for more attacks on their rights and urged Louis XVI throughout the Protests of the Parlement of Paris not to enact the proposed reforms.
These exemptions, as well as the right to wear a sword and their coat of arms, encouraged the idea of a natural superiority over the commoners that was common through the Second Estate, and as long as any noble was in possession of a fiefdom, they could collect a tax on the Third Estate called Feudal Dues, which would allegedly be for the Third Estate's protection (this only applied to serfs and tenants of farmland owned by the nobility). Overall, the Second Estate had vast privileges that the Third Estate did not possess, which in effect protected the Second Estate's wealth and property, while hindering the Third Estate's ability to advance. The reforms proposed by Turgot and argued against in the Protests of the Parlement of Paris conflicted with the Second Estates’ interests to keep their hereditary privileges, and was the first step toward reform that seeped into the political arena. Turgot's reforms were unpopular among the commoners as well, who saw the parlements as their best defense against the power of the monarchy.
Reaction
This behavior of the parlements is one of the reasons that since the French Revolution, French courts have been forbidden by Article 5 of the French civil code to create law and act as legislative bodies, their only mandate being to interpret the law. France, through the Napoleonic Code, was at the origin of the modern system of civil law in which precedents are not as powerful as in countries of common law. The origin of the separation of powers in the French court system, with no rule of precedent outside the interpretation of the law, no single supreme court and no constitutional review of statutes by courts until 1971 (by action, before the Constitutional Council of France created in 1958) and 2010 (by exception, before any court)[14] is usually traced to that hostility towards "government by judges".[15][16][17]
Judicial proceedings
In civil trials, judges had to be paid épices (literally "spices" – fees) by the parties. Civil justice was out of reach of most of the population, except the wealthiest and best connected.
Regarding criminal justice, the proceedings were markedly archaic. Judges could order suspects to be tortured in order to extract confessions or induce them to reveal the names of their accomplices: there were the question ordinaire ("ordinary questioning"), the ordinary form of torture, and the question extraordinaire ("extraordinary questioning"), with increased brutality. There was little presumption of innocence if the suspect was a mere poor commoner. The death sentence could be pronounced for a variety of crimes including mere theft; depending on the crime and the social class of the victim, death could be by decapitation with a sword (for nobles), hanging (for most of the secondary crimes by commoners), the breaking wheel (for some heinous crimes by commoners), and even burning at the stake (for heresy, or advocacy of atheism). Some crimes, such as regicide, exacted even more horrific punishment. With the spread of enlightenment ideas throughout France, most forms of judicial torture had fallen out of favor, and while they remained on the books, were rarely applied after 1750.
Ultimately, judicial torture and cruel methods of executions were abolished in 1788 by King Louis XVI.[18]
Current usage
In current French language usage, parlement means parliament as in the English expression Parliament of France. It is quite a different meaning than the role of the parlements under the Ancien Régime.
See also
Notes
- ↑ Alfred Cobban (1957). A History of France. 1. p. 63. see also Cobban, "The Parlements of France in the eighteenth century." History (1950) 35#123 pp 64-80.
- ↑ Paul R. Hanson (2007). The A to Z of the French Revolution. pp. 250–51.
- ↑ G. W. Prothero, "The Parliament [sic] of Paris", The English Historical Review, 13, No. 50 (April 1898), pp. 229-241.
- ↑ Mack P. Holt, "The King in Parliament: The Problem of the Lit de Justice in Sixteenth-Century France" The Historical Journal (September 1988( 32#3 pp:507-523.
- ↑ A. Lloyd Moote. The Revolt of the Judges: the Parlement of Paris and the Fronde, 1643-1652 (Princeton University Press, 1971)
- ↑ John J. Hurt, Louis XIV and the Parlements: The Assertion of Royal Authority (2002) p 195-96
- ↑ Dates and list based on Pillorget, vol 2, p. 894 and Jouanna p. 1183.
- ↑ Dabiel Roche, France in the Enlightenment (1998) pp 462-82
- ↑ Julian Swann, Politics and the Parlement of Paris under Louis XV, 1754-1774 (1995).
- ↑ William Doyle, "The Parlements of France and the Breakdown of the Old Regime 1771-1788." French Historical Studies (1970): 415-458 in JSTOR.
- ↑ Doyle, "The Parlements of France and the Breakdown of the Old Regime 1771-1788."
- ↑ John W. Boyer and Keith M. Baker, eds. (1987). University of Chicago Readings in Western Civilization, Volume 7: The Old Regime and the French Revolution. University of Chicago Press. pp. 119–21.
- ↑ In the Pays d'État, the taille was called réelle, based on land ownership, and determined by a council; in the Pays d'Élection the taille was called personnelle, based on the global capacity to pay, and assessed by the Intendant. In both cases, the tax was often considered arbitrary.
- ↑ The control of conventionality according to the European Convention on Human Rights was introduced in 1975 and 1989, respectively for judiciary and administrative courts.
- ↑ Michael H. Davis, The Law/Politics Distinction, the French Conseil Constitutionnel, and the U. S. Supreme Court, The American Journal of Comparative Law, Vol. 34, No. 1 (Winter, 1986), pp. 45-92
- ↑ James Beardsley, Constitutional Review in France, The Supreme Court Review, Vol. 1975, (1975), pp. 189-259
- ↑ Denis Tallon, John N. Hazard, George A. Bermann, The Constitution and the Courts in France, The American Journal of Comparative Law, Vol. 27, No. 4 (Autumn, 1979), pp. 567-587
- ↑ Abstract of dissertation "'Pour savoir la verité de sa bouche': The Practice and Abolition of Judicial Torture in the Parlement of Toulouse, 1600-1788" by Lisa Silverman.
Further reading
- Cobban, Alfred. "The Parlements of France in the eighteenth century." History 35.123 (1950): 64-80.
- Collins, James B. The state in early modern France (Cambridge University Press, 1995)
- Doyle, William. "The Parlements of France and the Breakdown of the Old Regime 1771-1788." French Historical Studies (1970): 415-458 in JSTOR.
- Holt, Mack P. "The King in Parliament: The Problem of the Lit de Justice in Sixteenth-Century France" Historical Journal (September 1988) 31#3 pp :507-523).
- Holt, Mack P., ed. Society and Institutions in Early Modern France (1991)
- Hurt, John J. Louis XIV and the Parlements: The Assertion of Royal Authority (Manchester University Press, 2002) online
- Jones, Colin. The Great Nation: France from Louis XV to Napoleon (2003)
- Ladurie, Emmanuel Le Roy. The Ancien Regime: A History of France, 1610 - 1774 (1998)
The Parlement of Paris
- Moote, A. Lloyd. The revolt of the judges: the Parlement of Paris and the Fronde, 1643-1652 (Princeton University Press, 1971)
- Prothero, G. W. "The Parlement of Paris," English Historical Review (1898) 13#50 229-241. in JSTOR
- Rogister, John. Louis XV and the Parlement of Paris, 1737-55 (Cambridge University Press, 2002)
- Shennan, J. H. "The Political Role of the Parlement of Paris, 1715-23," Historical Journal (1965) 8#2 pp. 179–200 in JSTOR
- Shennan, Joseph Hugh. The Parlement of Paris (1998).
- Stone, Bailey. The Parlement of Paris, 1774-1789 (University of North Carolina Press, 1981) online
- Swann, Julian. Politics and the Parlement of Paris under Louis XV, 1754-1774 (Cambridge University Press, 1995)
In French
- (French) Bluche, François. L'Ancien régime: Institutions et société. Collection: Livre de poche. Paris: Fallois, 1993. ISBN 2-253-06423-8
- (French) Jouanna, Arlette and Jacqueline Boucher, Dominique Biloghi, Guy Thiec. Histoire et dictionnaire des Guerres de Religion. Collection: Bouquins. Paris: Laffont, 1998. ISBN 2-221-07425-4
- (French) Pillorget, René and Suzanne Pillorget. France Baroque, France Classique 1589-1715. Collection: Bouquins. Paris: Laffont, 1995. ISBN 2-221-08110-2
- (French) Saint-Bonnet, François. “Le contrôle a posteriori : les parlements de l’Ancien Régime et la neutralisation de la loi”. Les Cahiers du Conseil constitutionnel, N° 28 (2010).