Polyethylene glycol
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
poly(oxyethylene) {structure-based}, poly(ethylene oxide) {source-based}[1] | |
| Other names
Carbowax, GoLYTELY, GlycoLax, Fortrans, TriLyte, Colyte, Halflytely, Macrogol, MiraLAX, MoviPrep | |
| Identifiers | |
| 25322-68-3 | |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL1201478 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.105.546 |
| E number | E1521 (additional chemicals) |
| UNII | 3WJQ0SDW1A |
| Properties | |
| C2nH4n+2On+1 | |
| Molar mass | 18.02 + 44.05n g/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| A06AD15 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 182 to 287 °C; 360 to 549 °F; 455 to 560 K |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
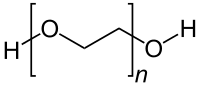
Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is a polyether compound with many applications from industrial manufacturing to medicine. PEG is also known as polyethylene oxide (PEO) or polyoxyethylene (POE), depending on its molecular weight. The structure of PEG is commonly expressed as H−(O−CH2−CH2)n−OH.
Available forms and nomenclature
PEG, PEO, or POE refers to an oligomer or polymer of ethylene oxide. The three names are chemically synonymous, but historically PEG is preferred in the biomedical field, whereas PEO is more prevalent in the field of polymer chemistry. Because different applications require different polymer chain lengths, PEG has tended to refer to oligomers and polymers with a molecular mass below 20,000 g/mol, PEO to polymers with a molecular mass above 20,000 g/mol, and POE to a polymer of any molecular mass.[2] PEG and PEO are liquids or low-melting solids, depending on their molecular weights. PEGs are prepared by polymerization of ethylene oxide and are commercially available over a wide range of molecular weights from 300 g/mol to 10,000,000 g/mol. While PEG and PEO with different molecular weights find use in different applications, and have different physical properties (e.g. viscosity) due to chain length effects, their chemical properties are nearly identical. Different forms of PEG are also available, depending on the initiator used for the polymerization process – the most common initiator is a monofunctional methyl ether PEG, or methoxypoly(ethylene glycol), abbreviated mPEG. Lower-molecular-weight PEGs are also available as purer oligomers, referred to as monodisperse, uniform, or discrete. Very high purity PEG has recently been shown to be crystalline, allowing determination of a crystal structure by x-ray diffraction.[3] Since purification and separation of pure oligomers is difficult, the price for this type of quality is often 10–1000 fold that of polydisperse PEG.
PEGs are also available with different geometries.
- Branched PEGs have three to ten PEG chains emanating from a central core group.
- Star PEGs have 10 to 100 PEG chains emanating from a central core group.
- Comb PEGs have multiple PEG chains normally grafted onto a polymer backbone.
The numbers that are often included in the names of PEGs indicate their average molecular weights (e.g. a PEG with n = 9 would have an average molecular weight of approximately 400 daltons, and would be labeled PEG 400. Most PEGs include molecules with a distribution of molecular weights (i.e. they are polydisperse). The size distribution can be characterized statistically by its weight average molecular weight (Mw) and its number average molecular weight (Mn), the ratio of which is called the polydispersity index (Mw/Mn). MW and Mn can be measured by mass spectrometry.
PEGylation is the act of covalently coupling a PEG structure to another larger molecule, for example, a therapeutic protein, which is then referred to as a PEGylated protein. PEGylated interferon alfa-2a or −2b are commonly used injectable treatments for hepatitis C infection.
PEG is soluble in water, methanol, ethanol, acetonitrile, benzene, and dichloromethane, and is insoluble in diethyl ether and hexane. It is coupled to hydrophobic molecules to produce non-ionic surfactants.[4]
PEGs contain potential toxic impurities, such as ethylene oxide and 1,4-dioxane. Ethylene Glycol and its ethers are nephrotoxic if applied to damaged skin.[5]
Polyethylene glycol (PEG) and related polymers (PEG phospholipid constructs) are often sonicated when used in biomedical applications. However, as reported by Murali et al., PEG is very sensitive to sonolytic degradation and PEG degradation products can be toxic to mammalian cells. It is, thus, imperative to assess potential PEG degradation to ensure that the final material does not contain undocumented contaminants that can introduce artifacts into experimental results.[6]
PEGs and methoxypolyethylene glycols are manufactured by Dow Chemical under the tradename Carbowax for industrial use, and Carbowax Sentry for food and pharmaceutical use. They vary in consistency from liquid to solid, depending on the molecular weight, as indicated by a number following the name. They are used commercially in numerous applications, including as surfactants, in foods, in cosmetics, in pharmaceutics, in biomedicine, as dispersing agents, as solvents, in ointments, in suppository bases, as tablet excipients, and as laxatives. Some specific groups are lauromacrogols, nonoxynols, octoxynols, and poloxamers.
Macrogol, used as a laxative, is a form of polyethylene glycol. The name may be followed by a number which represents the average molecular weight (e.g. macrogol 3350, macrogol 4000 or macrogol 6000).
Production


Polyethylene glycol is produced by the interaction of ethylene oxide with water, ethylene glycol, or ethylene glycol oligomers.[7] The reaction is catalyzed by acidic or basic catalysts. Ethylene glycol and its oligomers are preferable as a starting material instead of water, because they allow the creation of polymers with a low polydispersity (narrow molecular weight distribution). Polymer chain length depends on the ratio of reactants.
- HOCH2CH2OH + n(CH2CH2O) → HO(CH2CH2O)n+1H
Depending on the catalyst type, the mechanism of polymerization can be cationic or anionic. The anionic mechanism is preferable because it allows one to obtain PEG with a low polydispersity. Polymerization of ethylene oxide is an exothermic process. Overheating or contaminating ethylene oxide with catalysts such as alkalis or metal oxides can lead to runaway polymerization, which can end in an explosion after a few hours.
Polyethylene oxide, or high-molecular weight polyethylene glycol, is synthesized by suspension polymerization. It is necessary to hold the growing polymer chain in solution in the course of the polycondensation process. The reaction is catalyzed by magnesium-, aluminium-, or calcium-organoelement compounds. To prevent coagulation of polymer chains from solution, chelating additives such as dimethylglyoxime are used.
Alkaline catalysts such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), or sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) are used to prepare low-molecular-weight polyethylene glycol.
Uses
Medical uses
- PEG is the basis of a number of laxatives. Whole bowel irrigation with polyethylene glycol and added electrolytes is used for bowel preparation before surgery or colonoscopy.
- PEG is also used as an excipient in many pharmaceutical products.
- When attached to various protein medications, polyethylene glycol allows a slowed clearance of the carried protein from the blood.[8]
Chemical uses
- Polyethylene glycol has a low toxicity and is used in a variety of products.[9] The polymer is used as a lubricating coating for various surfaces in aqueous and non-aqueous environments.[10]
- Since PEG is a flexible, water-soluble polymer, it can be used to create very high osmotic pressures (on the order of tens of atmospheres). It also is unlikely to have specific interactions with biological chemicals. These properties make PEG one of the most useful molecules for applying osmotic pressure in biochemistry and biomembranes experiments, in particular when using the osmotic stress technique.
- Polyethylene glycol is also commonly used as a polar stationary phase for gas chromatography, as well as a heat transfer fluid in electronic testers.
- PEG has also been used to preserve objects that have been salvaged from underwater, as was the case with the warship Vasa in Stockholm,[11] the Mary Rose in England, the Ma'agan Michael Ship in Israel,[12] and artifacts from the Steamboat Arabia in Kansas City, Missouri.[13] It replaces water in wooden objects, making the wood dimensionally stable and preventing warping or shrinking of the wood when it dries. In addition, PEG is used when working with green wood as a stabilizer, and to prevent shrinkage.[14]
- PEG has been used to preserve the painted colors on Terra-Cotta Warriors unearthed at a UNESCO World Heritage site in China.[15] These painted artifacts were created during the Qin Shi Huang Di dynasty (first emperor of China). Within 15 seconds of the terra-cotta pieces being unearthed during excavations, the lacquer beneath the paint begins to curl after being exposed to the dry Xian air. The paint would subsequently flake off in about four minutes. The German Bavarian State Conservation Office developed a PEG preservative that when immediately applied to unearthed artifacts has aided in preserving the colors painted on the pieces of these clay soldiers.[16]
- PEG is often used (as an internal calibration compound) in mass spectrometry experiments, with its characteristic fragmentation pattern allowing accurate and reproducible tuning.
- PEG derivatives, such as narrow range ethoxylates, are used as surfactants.
- PEG has been used as the hydrophilic block of amphiphilic block copolymers used to create some polymersomes.[17]
Biological uses
- PEG is commonly used as a precipitant for plasmid DNA isolation and protein crystallization. X-ray diffraction of protein crystals can reveal the atomic structure of the proteins.
- PEG is used to fuse two different types of cells, most often B-cells and myelomas in order to create hybridomas.
- Polymer segments derived from PEG polyols impart flexibility to polyurethanes for applications such as elastomeric fibers (spandex) and foam cushions.
- In microbiology, PEG precipitation is used to concentrate viruses. PEG is also used to induce complete fusion (mixing of both inner and outer leaflets) in liposomes reconstituted in vitro.
- Gene therapy vectors (such as viruses) can be PEG-coated to shield them from inactivation by the immune system and to de-target them from organs where they may build up and have a toxic effect.[18] The size of the PEG polymer has been shown to be important, with larger polymers achieving the best immune protection.
- PEG is a component of stable nucleic acid lipid particles (SNALPs) used to package siRNA for use in vivo.[19][20]
- In blood banking, PEG is used as a potentiator to enhance detection of antigens and antibodies.[21]
- When working with phenol in a laboratory situation, PEG 300 can be used on phenol skin burns to deactivate any residual phenol.
Commercial uses
- PEG is the basis of many skin creams (as cetomacrogol) and personal lubricants (frequently combined with glycerin).
- PEG is used in a number of toothpastes as a dispersant. In this application, it binds water and helps keep xanthan gum uniformly distributed throughout the toothpaste.
- PEG is also under investigation for use in body armor, and in tattoos to monitor diabetes.[22][23]
- In low-molecular-weight formulations (i.e. PEG 400), it is used in Hewlett-Packard designjet printers as an ink solvent and lubricant for the print heads.
- PEG is also one of the main ingredients in paintball fills, because of its thickness and flexibility. However, as early as 2006, some Paintball manufacturers began substituting cheaper oil-based alternatives for PEG.
- PEG is also used as an anti-foaming agent in food[24] – its INS number is 1521[25] or E1521 in the EU.[26]
Industrial uses
- Nitrate ester-plasticized polyethylene glycol is used in Trident II submarine-launched ballistic missile solid rocket fuel.[27]
- Dimethyl ethers of PEG are the key ingredient of Selexol, a solvent used by coal-burning, integrated gasification combined cycle (IGCC) power plants to remove carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide from the gas waste stream.
- PEG has been used as the gate insulator in an electric double-layer transistor to induce superconductivity in an insulator.[28]
- PEG is also used as a polymer host for solid polymer electrolytes. Although not yet in commercial production, many groups around the globe are engaged in research on solid polymer electrolytes involving PEG, with the aim of improving their properties, and in permitting their use in batteries, electro-chromic display systems, and other products in the future.
- PEG is injected into industrial processes to reduce foaming in separation equipment.
- PEG is used as a binder in the preparation of technical ceramics.[29]
Health effects
PEG is generally considered biologically inert and safe. However, a minority of people are allergic to it. Allergy to PEG is usually discovered after a person has been diagnosed with an allergy to an increasing number of seemingly unrelated products, including processed foods, cosmetics, drugs, and other substances that contain PEG or were manufactured with PEG.[30]
See also
- Ethylene
- Propylene glycol
- Monoethylene glycol
- Diethylene glycol
- PEGylation
- PEG-PVA
- Lauryl methyl gluceth-10 hydroxypropyl dimonium chloride
References
- ↑ Kahovec, J.; Fox, R. B.; Hatada, K. (2002). "Nomenclature of regular single-strand organic polymers". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 74 (10): 1921–1956. doi:10.1351/pac200274101921.
- ↑ For example, in the online catalog of Scientific Polymer Products, Inc., poly(ethylene glycol) molecular weights run up to about 20,000, while those of poly(ethylene oxide) have six or seven digits.
- ↑ French, Alister C.; Thompson, Amber L.; Davis, Benjamin G. (2009). "High Purity Discrete PEG Oligomer Crystals Allow Structural Insight" (PDF). Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 48 (7): 1248–1252. doi:10.1002/anie.200804623. PMID 19142918.
- ↑ Winger, Moritz; De Vries, Alex H.; Van Gunsteren, Wilfred F. (2009). "Force-field dependence of the conformational properties of α,ω-dimethoxypolyethylene glycol". Molecular Physics. 107 (13): 1313. doi:10.1080/00268970902794826.
- ↑ Andersen, F. A. (1999). "Special Report: Reproductive and Developmental Toxicity of Ethylene Glycol and Its Ethers". International Journal of Toxicology. 18 (3): 53–10. doi:10.1177/109158189901800208.
- ↑ Murali, V. S.; Wang, R.; Mikoryak, C. A.; Pantano, P.; Draper, R. (2015). "Rapid detection of polyethylene glycol sonolysis upon functionalization of carbon nanomaterials". Experimental Biology and Medicine. 240 (9): 1147–1151. doi:10.1177/1535370214567615. PMC 4527952
 . PMID 25662826.
. PMID 25662826. - ↑ Polyethylene glycol, Chemindustry.ru
- ↑ Bowman, Lee (4 December 2004). "Study on dogs yields hope in human paralysis treatment". seattlepi.com.
- ↑ Sheftel, Victor O. (2000). Indirect Food Additives and Polymers: Migration and Toxicology. CRC. pp. 1114–1116.
- ↑ Nalam, Prathima C.; Clasohm, Jarred N.; Mashaghi, Alireza; Spencer, Nicholas D. (2009). "Macrotribological Studies of Poly(L-lysine)-graft-Poly(ethylene glycol) in Aqueous Glycerol Mixtures". Tribology Letters. 37 (3): 541–552. doi:10.1007/s11249-009-9549-9.
- ↑ Lars-Åke Kvarning, Bengt Ohrelius (1998), The Vasa – The Royal Ship, ISBN 91-7486-581-1, pp. 133–141
- ↑ Linder, Elisha (1992). "Excavating an Ancient Merchantman". Biblical Archaeology Review. Biblical Archaeology Society. 18 (6): 24–35.
- ↑ Hawley, Greg (2005). Treasure in a Cornfield, p. 175-186. Paddle Wheel Publishing, Kansas City. ISBN 0965761258.
- ↑ Anti-Freeze is Not a Green Wood Stabilizer – Buzz Saw, The Rockler Blog. Rockler.com (2 May 2006). Retrieved on 30 November 2012.
- ↑ Reiffert, Stefanie (18 March 2015). "Conservators preserve the paint layers of the Terracotta Army". www.tum.de. Technische Universität München. Retrieved 19 December 2015.
- ↑ Larmer, Brook (June 2012). "Terra-Cotta Warriors in Color". National Geographic. 221 (6): 74–87.
- ↑ Rameez, Shahid; Alosta, Houssam; Palmer, Andre F. (2008). "Biocompatible and Biodegradable Polymersome Encapsulated Hemoglobin: A Potential Oxygen Carrier". Bioconjugate Chemistry. 19 (5): 1025–32. doi:10.1021/bc700465v. PMID 18442283.
- ↑ Kreppel, Florian; Kochanek, Stefan (2007). "Modification of Adenovirus Gene Transfer Vectors With Synthetic Polymers: A Scientific Review and Technical Guide". Molecular Therapy. 16 (1): 16–29. doi:10.1038/sj.mt.6300321. PMID 17912234.
- ↑ Rossi, J.J. (2006). "RNAi therapeutics: SNALPing siRNAs in vivo". Gene Therapy. 13 (7): 583–584. doi:10.1038/sj.gt.3302661. PMID 17526070.
- ↑ Geisbert, Thomas W.; Lee, Amy CH; Robbins, Marjorie; Geisbert, Joan B; Honko, Anna N; Sood, Vandana; Johnson, Joshua C; De Jong, Susan; et al. (29 May 2010). "Postexposure protection of non-human primates against a lethal Ebola virus challenge with RNA interference: a proof-of-concept study". The Lancet. 375 (9729): 1896–905. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60357-1. PMID 20511019. (free with registration)
- ↑ Harmening, Denise M. (2005). Modern Blood Banking & Transfusion Practices. F. A. Davis Company. ISBN 0-8036-1248-6.
- ↑ Johnson, Tonya (21 April 2004). "Army Scientists, Engineers develop Liquid Body Armor".
- ↑ "Tattoo to monitor diabetes". BBC News. 1 September 2002.
- ↑ US Government – Food and Drug Agency "Listing of Food Additive Status Part II". Retrieved 21 October 2011.
- ↑ "Codex Alimentarius". codexalimentarius.net. Archived from the original on 7 January 2012.
- ↑ "Current EU approved additives and their E Numbers". UK Government – Food Standards Agency. Retrieved 21 October 2010.
- ↑ Spinardi, Graham (1994). From Polaris to Trident : the development of US fleet ballistic missile technology. Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. Press. p. 159. ISBN 0-521-41357-5.
- ↑ Ueno, K.; Nakamura, S.; Shimotani, H.; Ohtomo, A.; Kimura, N.; Nojima, T.; Aoki, H.; Iwasa, Y.; Kawasaki, M. (2008). "Electric-field-induced superconductivity in an insulator". Nature Materials. 7 (11): 855–858. Bibcode:2008NatMa...7..855U. doi:10.1038/nmat2298. PMID 18849974.
- ↑ Schneider, Samuel J. (1991) Engineered Materials Handbook: Ceramics and Glasses, Vol. 4. ASM International. ISBN 0-87170-282-7. p. 49.
- ↑ Wenande, E.; Garvey, L. H. (2016-07-01). "Immediate-type hypersensitivity to polyethylene glycols: a review". Clinical and Experimental Allergy: Journal of the British Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 46 (7): 907–922. doi:10.1111/cea.12760. PMID 27196817.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Poly(ethylene glycol). |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Polyethylene glycols. |

