RAF kinase
RAF kinases are a family of three serine/threonine-specific protein kinases that are related to retroviral oncogenes.[11] The mouse sarcoma virus 3611 contains a RAF kinase-related oncogene that enhances fibrosarcoma induction. RAF is an acronym for Rapidly Accelerated Fibrosarcoma.[12]
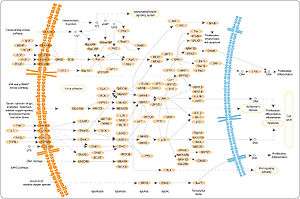
RAF kinases participate in the RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK signal transduction cascade, also referred to as the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade.[11] Activation of RAF kinases requires interaction with RAS-GTPases.
The three RAF kinase family members are:
References
- ↑ Rossomando AJ, Payne DM, Weber MJ, Sturgill TW (1989). "Evidence that pp42, a major tyrosine kinase target protein, is a mitogen-activated serine/threonine protein kinase". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 86 (18): 6940–3. doi:10.1073/pnas.86.18.6940. PMC 297966
 . PMID 2550926.
. PMID 2550926. - ↑ Bonni A, Brunet A, West AE, Datta SR, Takasu MA, Greenberg ME (1999). "Cell survival promoted by the Ras-MAPK signaling pathway by transcription-dependent and -independent mechanisms". Science. 286 (5443): 1358–62. doi:10.1126/science.286.5443.1358. PMID 10558990.
- ↑ Chadee DN, Yuasa T, Kyriakis JM (2002). "Direct activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase MEKK1 by the Ste20p homologue GCK and the adapter protein TRAF2". Mol. Cell. Biol. 22 (3): 737–49. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.3.737-749.2002. PMC 133545
 . PMID 11784851.
. PMID 11784851. - ↑ Chang L, Karin M (2001). "Mammalian MAP kinase signaling cascades". Nature. 410 (6824): 37–40. doi:10.1038/35065000. PMID 11242034.
- ↑ Chen YR, Tan TH (2000). "The c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway and apoptotic signaling (review)". Int. J. Oncol. 16 (4): 651–62. doi:10.3892/ijo.16.4.651. PMID 10717232.
- ↑ Hazzalin CA, Mahadevan LC (2002). "MAPK-regulated transcription: a continuously variable gene switch?". Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3 (1): 30–40. doi:10.1038/nrm715. PMID 11823796.
- ↑ Kato Y, Kravchenko VV, Tapping RI, Han J, Ulevitch RJ, Lee JD (1997). "BMK1/ERK5 regulates serum-induced early gene expression through transcription factor MEF2C". EMBO J. 16 (23): 7054–66. doi:10.1093/emboj/16.23.7054. PMC 1170308
 . PMID 9384584.
. PMID 9384584. - ↑ Kiefer F, Tibbles LA, Anafi M, Janssen A, Zanke BW, Lassam N, Pawson T, Woodgett JR, Iscove NN (1996). "HPK1, a hematopoietic protein kinase activating the SAPK/JNK pathway". EMBO J. 15 (24): 7013–25. PMC 452527
 . PMID 9003777.
. PMID 9003777. - ↑ Pearson G, English JM, White MA, Cobb MH (2001). "ERK5 and ERK2 cooperate to regulate NF-kappaB and cell transformation". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (11): 7927–31. doi:10.1074/jbc.M009764200. PMID 11118448.
- ↑ Weston CR, Lambright DG, Davis RJ (2002). "Signal transduction. MAP kinase signaling specificity". Science. 296 (5577): 2345–7. doi:10.1126/science.1073344. PMID 12089430.
- 1 2 Roskoski R (August 2010). "RAF protein-serine/threonine kinases: structure and regulation" (PDF). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 399 (3): 313–7. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.07.092. PMID 20674547.
- ↑ Zebisch A, Troppmair J (June 2006). "Back to the roots: the remarkable RAF oncogene story". Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 63 (11): 1314–30. doi:10.1007/s00018-006-6005-y. PMID 16649144.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/13/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.