First inversion
The first inversion of a chord is the voicing of a triad, seventh chord, or ninth chord with the third of the chord in the bass and the root a sixth above it.[1] In the first inversion of a C-major triad ![]() Play , the bass is E—the third of the triad—with the fifth and the root stacked above it (the root now shifted an octave higher), forming the intervals of a third and a sixth above the inverted bass of E, respectively.
Play , the bass is E—the third of the triad—with the fifth and the root stacked above it (the root now shifted an octave higher), forming the intervals of a third and a sixth above the inverted bass of E, respectively.

Root position, first inversion, and second inversion C major chords 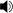 Play root position C major chord ,
Play root position C major chord , 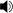 Play first inversion C major chord , or
Play first inversion C major chord , or 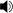 Play second inversion C major chord . Chord roots (all the same) in red.
Play second inversion C major chord . Chord roots (all the same) in red.
F major chord

First inversion.

Second inversion.
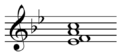
Third inversion F7 chord 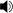 Play .
Play .

See also
References
- ↑ Walter Piston, Harmony, fifth edition, revised and expanded by Mark DeVoto (New York: W. W. Norton, 1987): p. 66. ISBN 978-0-393-95480-7.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 2/21/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.