Norgestrienone
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | G03AC07 (WHO) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms | RU-2010 |
| CAS Number |
848-21-5 |
| PubChem (CID) | 13313 |
| ChemSpider |
12749 |
| UNII |
89386PYU9O |
| KEGG |
D07220 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H22O2 |
| Molar mass | 294.387 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
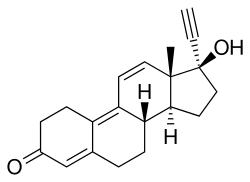
Norgestrienone (INN) (brand name Ogyline, Planor, Miniplanor; former developmental code name RU-2010), also known as Δ9,11-norethisterone[1] or 17α-ethynyltrienolone (17α-ethynyltrenbolone), as well as 17α-ethynylestra-4,9,11-trien-17β-ol-3-one, is a steroidal progestin related to norethisterone that is used as a hormonal contraceptive, sometimes in combination with ethinyl estradiol.[2][3][4][5] It was developed by Roussel Uclaf and is registered for use only in France.[5][6] Under the brand name Planor, it is or was marketed in France as 2 mg norgestrienone and 50 μg ethinyl estradiol tablets.[7] Norgestrienone has been found to possess similar affinity for the progesterone receptor and androgen receptor,[8] and in accordance, has some androgenic activity.[9][10][11] The drug was first described in the literature in 1965.[10] Gestrinone is the 13β-ethyl variant or 18-methyl derivative of norgestrienone.[12]
See also
References
- ↑ J.P. Lavery; J.S. Sanfilippo (6 December 2012). Pediatric and Adolescent Obstetrics and Gynecology. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 236–. ISBN 978-1-4612-5064-7.
- ↑ J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 887–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ↑ I.K. Morton; Judith M. Hall (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 202–. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1.
- ↑ Diaz, S.; Pavez, M.; Quinteros, E.; Diaz, J.; Robertson, D. N.; Croxatto, H. B. (1978). "Clinical trial with subdermal implants containing norgestrienone". Contraception. 18 (4): 429–440. doi:10.1016/0010-7824(78)90027-6. PMID 720075.
- 1 2 Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 751–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- ↑ John L. McGuire (2000). Pharmaceuticals, 4 Volume Set. Wiley. p. 1580,1599. ISBN 978-3-527-29874-7.
- ↑ IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; World Health Organization; International Agency for Research on Cancer (2007). Combined Estrogen-progestogen Contraceptives and Combined Estrogen-progestogen Menopausal Therapy. World Health Organization. pp. 455–. ISBN 978-92-832-1291-1.
- ↑ Loughney DA, Schwender CF (1992). "A comparison of progestin and androgen receptor binding using the CoMFA technique". J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 6 (6): 569–81. PMID 1291626.
- ↑ Julius Axelrod (1 January 1982). Biochemical Actions of Hormones. Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-452809-3.
- 1 2 Christian Lauritzen; John W. W. Studd (22 June 2005). Current Management of the Menopause. CRC Press. pp. 45–. ISBN 978-0-203-48612-2.
- ↑ R.T. Di Giulio; E. Monosson (6 December 2012). Interconnections Between Human and Ecosystem Health. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 60–. ISBN 978-94-009-1523-7.
- ↑ Victor Gomel; Andrew Brill (27 September 2010). Reconstructive and Reproductive Surgery in Gynecology. CRC Press. pp. 90–. ISBN 978-1-84184-757-3.