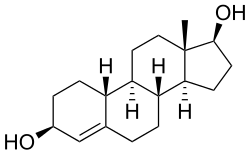
Bolandiol
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | 19-Norandrostenediol; 19-Nor-4-androstene-3β,17β-diol; Estr-4-ene-3β,17β-diol; 3β-Dihydronandrolone |
| CAS Number | 19793-20-5 |
| PubChem (CID) | 9835303 |
| ChemSpider | 8011024 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL2106664 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H28O2 |
| Molar mass | 276.42 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
Bolandiol (INN), also known as 19-nor-4-androstenediol, estr-4-en-3β,17β-diol, or 3β-dihydronandrolone, is an anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) that was never marketed.[1] A dipropionate ester, bolandiol dipropionate (brand names Anabiol, Storinal; former developmental code name SC-7525), has been marketed.[1][2] Bolandiol (and its dipropionate ester) is unique among AAS in that it reportedly also possesses estrogenic and progestogenic activity.[3][4]
Bolandiol is on the World Anti-Doping Agency's list of prohibited substances,[5] and is therefore banned from use in most major sports. It is a potential metabolic precursor to nandrolone.[6] However, several clinical studies have concluded that bolandiol does not alter strength, body composition, or exercise performance.[7][8]
See also
- 4-Androstenediol
- 19-Nor-5-androstenediol
- 19-Nor-5-androstenedione
- Bolandione (19-nor-4-androstenedione)
- Bolenol (17α-ethyl-19-nor-5-androstenol)
References
- 1 2 J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 899–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ↑ Thomas E. Hyde; Marianne S. Gengenbach (2007). Conservative Management of Sports Injuries. Jones & Bartlett Learning. pp. 1100–. ISBN 978-0-7637-3252-3.
- ↑ Hormones: Advances in Research and Application: 2011 Edition. ScholarlyEditions. 9 January 2012. pp. 59–. ISBN 978-1-4649-2242-8.
- ↑ Attardi, BJ; Page, ST; Hild, SA; Coss, CC; Matsumoto, AM (2010). "Mechanism of action of bolandiol (19-nortestosterone-3beta,17beta-diol), a unique anabolic steroid with androgenic, estrogenic, and progestational activities". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 118 (3): 151–61. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2009.11.008. PMC 2831543
 . PMID 19941958.
. PMID 19941958. - ↑ "The World Anti-Doping Code: The 2012 Prohibited List" (PDF). World Anti-Doping Agency. Retrieved 2012-07-17.
- ↑ Dehennin, L.; Bonnaire, Y.; Plou, Ph. (2002). "Human nutritional supplements in the horse: comparative effects of 19-norandrostenedione and 19-norandrostenediol on the 19-norsteroid profile and consequences for doping control". Journal of Chromatography B. 766 (2): 257–263. doi:10.1016/S0378-4347(01)00506-0.
- ↑ Van Gammeren, D; Falk, D; Antonio, J (2001). "The effects of supplementation with 19-nor-4-androstene-3,17-dione and 19-nor-4-androstene-3,17-diol on body composition and athletic performance in previously weight-trained male athletes". European journal of applied physiology. 84 (5): 426–31. doi:10.1007/s004210100395. PMID 11417430.
- ↑ Van Gammeren, D; Falk, D; Antonio, J (2002). "Effects of norandrostenedione and norandrostenediol in resistance-trained men". Nutrition. 18 (9): 734–7. doi:10.1016/s0899-9007(02)00834-1. PMID 12297208.
| AR |
| ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPRC6A |
| ||||||||||
See also: Estrogenics • Glucocorticoidics • Mineralocorticoidics • Progestogenics • Steroid hormone metabolism modulators • List of androgens/anabolic steroids | |||||||||||
| ER |
| ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPER |
| ||||||||||
See also: Androgenics • Glucocorticoidics • Mineralocorticoidics • Progestogenics • Steroid hormone metabolism modulators | |||||||||||
| PR |
| ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mPRs (PAQRs) |
| ||||||||||
See also: Androgenics • Estrogenics • Glucocorticoidics • Mineralocorticoidics • Steroid hormone metabolism modulators | |||||||||||