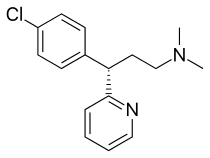
Dexchlorpheniramine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Chlor-trimeton |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682543 |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | R06AB02 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
25523-97-1 |
| PubChem (CID) | 33036 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 1210 |
| DrugBank |
DB01114 |
| ChemSpider |
30576 |
| UNII |
3Q9Q0B929N |
| KEGG |
D07803 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:4464 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1201353 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.042.779 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H19ClN2 |
| Molar mass | 274.788 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Dexchlorpheniramine (trade name Polaramine) is an antihistamine with anticholinergic properties used to treat allergic conditions such as hay fever or urticaria.[1][2] It is the pharmacologically active dextrorotatory isomer of chlorpheniramine.
References
- ↑ Theunissen, E. L.; Vermeeren, A.; Ramaekers, J. G. (2006). "Repeated-dose effects of mequitazine, cetirizine and dexchlorpheniramine on driving and psychomotor performance". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 61 (1): 79–86. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2005.02524.x. PMC 1884990
 . PMID 16390354.
. PMID 16390354. - ↑ Ortíz San Román, L.; Sanavia Morán, E.; Campos Domínguez, M.; Peinador García, M. M. (2013). "Síndrome anticolinérgico por dexclorfeniramina como causa de retención urinaria". Anales de Pediatría. 79 (6): 400–1. doi:10.1016/j.anpedi.2013.02.014. PMID 23680058.
External links
| Aminoalkyl ethers |
|
|---|---|
| Substituted alkylamines | |
| Substituted ethylenediamines |
|
| Phenothiazine derivatives | |
| Piperazine derivatives | |
| Others for systemic use |
|
| For topical use | |
| Receptor (ligands) |
| ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transporter (inhibitors) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Enzyme (inhibitors) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 4/27/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.