Solar eclipse of December 12, 1871
| Solar eclipse of December 12, 1871 | |
|---|---|
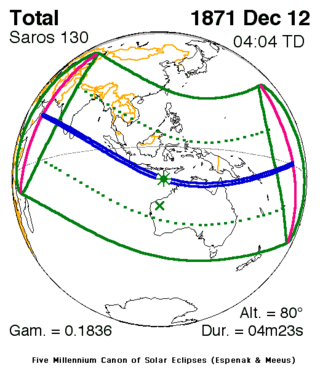 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | 0.1836 |
| Magnitude | 1.0465 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 263 sec (4 m 23 s) |
| Coordinates | 12°42′S 119°24′E / 12.7°S 119.4°E |
| Max. width of band | 157 km (98 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 4:03:38 |
| References | |
| Saros | 130 (44 of 73) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9215 |
A total solar eclipse occurred on December 12, 1871. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.
Observations

Related eclipses
Saros 130
It is a part of Saros cycle 130, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, containing 73 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on August 20, 1096. It contains total eclipses from April 5, 1475 through July 18, 2232. The series ends at member 73 as a partial eclipse on October 25, 2394. The longest duration of totality was 6 minutes, 41 seconds on July 11, 1619.[1]
| Series members 43–56 between 1853 and 2100 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 43 | 44 | 45 |
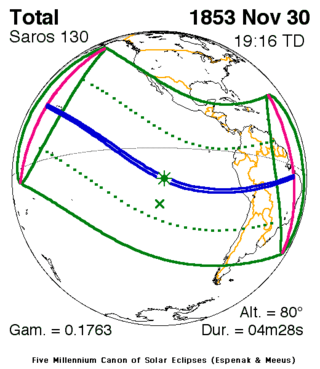 November 30, 1853 |
 December 12, 1871 |
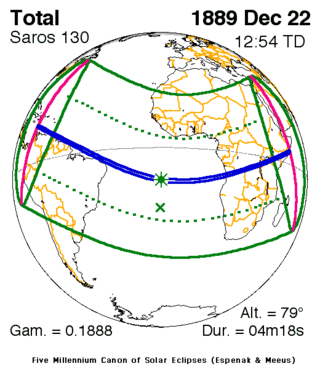 December 22, 1889 |
| 46 | 47 | 48 |
 January 3, 1908 |
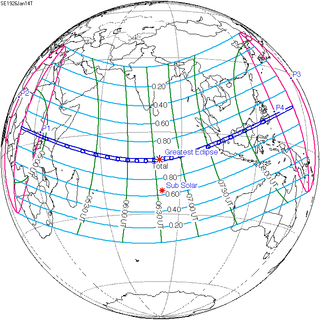 January 14, 1926 |
 January 25, 1944 |
| 49 | 50 | 51 |
 February 5, 1962 |
 February 16, 1980 |
 February 26, 1998 |
| 52 | 53 | 54 |
 March 9, 2016 |
 March 20, 2034 |
 March 30, 2052 |
| 55 | 56 | |
 April 11, 2070 |
 April 21, 2088 | |
References
- NASA chart graphics
- Sketch of Solar Corona 1871 December 12
- Total Eclipses of the Sun by Mabel Loomis Todd, 1900
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 1871 December 12. |
