Solar eclipse of July 11, 1991
| Solar eclipse of July 11, 1991 | |
|---|---|
|
Totality from Playas del Coco, Costa Rica | |
 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | -0.0041 |
| Magnitude | 1.08 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 413 sec (6 m 53 s) |
| Coordinates | 22°00′N 105°12′W / 22°N 105.2°W |
| Max. width of band | 258 km (160 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| (P1) Partial begin | 16:28:46 |
| (U1) Total begin | 17:21:41 |
| Greatest eclipse | 19:07:01 |
| (U4) Total end | 20:50:28 |
| (P4) Partial end | 21:43:24 |
| References | |
| Saros | 136 (36 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9489 |
A total solar eclipse occurred on July 11, 1991. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality began over the Pacific Ocean and Hawaii moving across Mexico, down through Central America and across South America ending over Brazil. It lasted for 6 minutes and 53 seconds at the point of maximum eclipse. There will not be a longer total eclipse until June 13, 2132.
This eclipse was the most central total eclipse in 800 years, with a gamma of -.0041. There will not be a more central eclipse for another 800 years. Its magnitude was also greater than any eclipse since the 6th century.
Observations
 Animation of eclipse path
Animation of eclipse path
 Partial phase before totality as seen through the cloud cover, Playas del Coco, Guanacaste, Costa Rica
Partial phase before totality as seen through the cloud cover, Playas del Coco, Guanacaste, Costa Rica
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses 1990-1992
Each member in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1990–1992 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||
| Saros | Map | Saros | Map | |
| 121 | January 26, 1990 Annular |
126 | July 22, 1990 Total | |
| 131 | January 15, 1991 Annular |
136 | July 11, 1991 Total | |
| 141 | January 4, 1992 Annular |
146 | June 30, 1992 Total | |
| 151 | December 24, 1992 Partial |
|||
Saros 136
Solar Saros 136, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, contains 71 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on Jun 14, 1360, and reached a first annular eclipse on September 8, 1504. It was a hybrid event from November 22, 1612, through January 17, 1703, and total eclipses from January 27, 1721 through May 13, 2496. The series ends at member 71 as a partial eclipse on July 30, 2622, with the entire series lasting 1262 years. The longest eclipse occurred on June 20, 1955, with a maximum duration of totality at 7 minutes, 8 seconds.[1]
| Series members 29–43 occur between 1865 and 2117 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
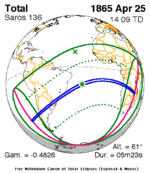 April 25, 1865 |
 May 6, 1883 |
 May 18, 1901 |
| 32 | 33 | 34 |
 May 29, 1919 |
 Jun 8, 1937 |
 Jun 20, 1955 |
| 35 | 36 | 37 |
 Jun 30, 1973 |
 Jul 11, 1991 |
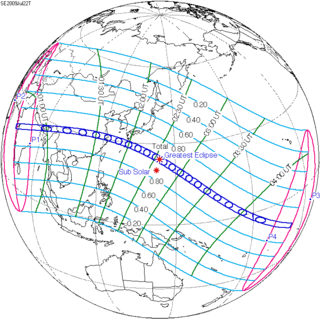 Jul 22, 2009 |
| 38 | 39 | 40 |
 Aug 2, 2027 |
 Aug 12, 2045 |
 Aug. 24, 2063 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 |
 Sep. 3, 2081 |
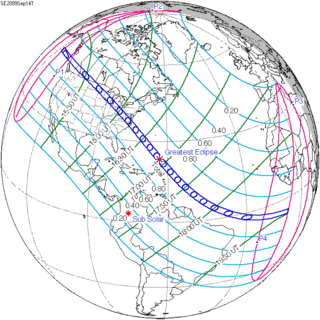 Sep. 14, 2099 |
 Sep. 26, 2117 |
Inex series
This eclipse is a part of the long period inex cycle, repeating at alternating nodes, every 358 synodic months (≈ 10,571.95 days, or 29 years minus 20 days). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee). However, groupings of 3 inex cycles (≈ 87 years minus 2 months) comes close (≈ 1,151.02 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Inex series members between 1901 and 2100: | ||
|---|---|---|
 September 9, 1904 (Saros 133) |
 August 21, 1933 (Saros 134) |
 July 31, 1962 (Saros 135) |
 July 11, 1991 (Saros 136) |
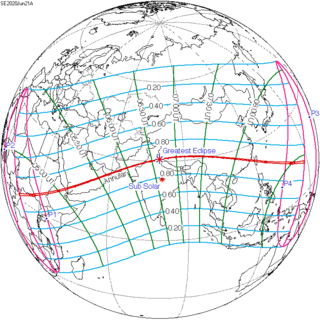 June 21, 2020 (Saros 137) |
 May 31, 2049 (Saros 138) |
 May 11, 2078 (Saros 139) |
||
Tritos series
This eclipse is a part of a tritos cycle, repeating at alternating nodes every 135 synodic months (≈ 3986.63 days, or 11 years minus 1 month). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee), but groupings of 3 tritos cycles (≈ 33 years minus 3 months) come close (≈ 434.044 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Series members between 1901 and 2100 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 March 17, 1904 (Saros 128) |
 February 14, 1915 (Saros 129) |
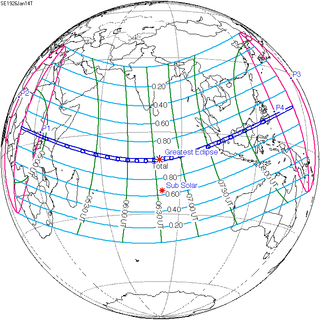 January 14, 1926 (Saros 130) | |
 December 13, 1936 (Saros 131) |
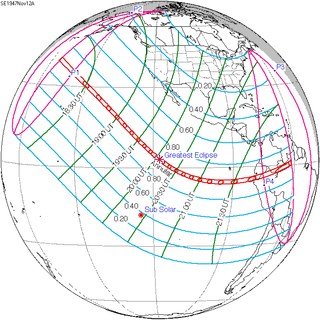 November 12, 1947 (Saros 132) |
 October 12, 1958 (Saros 133) | |
 September 11, 1969 (Saros 134) |
 August 10, 1980 (Saros 135) |
 July 11, 1991 (Saros 136) | |
 June 10, 2002 (Saros 137) |
 May 10, 2013 (Saros 138) |
 April 8, 2024 (Saros 139) | |
 March 9, 2035 (Saros 140) |
 February 5, 2046 (Saros 141) |
 January 5, 2057 (Saros 142) | |
 December 6, 2067 (Saros 143) |
 November 4, 2078 (Saros 144) |
 October 4, 2089 (Saros 145) | |
 September 4, 2100 (Saros 146) |
|||
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days).
| 21 eclipse events, progressing from north to south between July 11, 1953 and July 11, 2029 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| July 10-11 | April 29-30 | February 15-16 | December 4 | September 21-23 |
| 116 | 118 | 120 | 122 | 124 |
 July 11, 1953 |
 April 30, 1957 |
 February 15, 1961 |
 December 4, 1964 |
 September 22, 1968 |
| 126 | 128 | 130 | 132 | 134 |
 July 10, 1972 |
 April 29, 1976 |
 February 16, 1980 |
 December 4, 1983 |
 September 23, 1987 |
| 136 | 138 | 140 | 142 | 144 |
 July 11, 1991 |
 April 29, 1995 |
 February 16, 1999 |
 December 4, 2002 |
 September 22, 2006 |
| 146 | 148 | 150 | 152 | 154 |
 July 11, 2010 |
 April 29, 2014 |
 February 15, 2018 |
 December 4, 2021 |
 September 21, 2025 |
| 156 | ||||
 July 11, 2029 | ||||
Notes
References
- NASA graphics
- Observer's handbook 1991, Editor Roy L. Bishop, The Royal Astronomical Society of Canada (p. 101)
Photos:
- Russian scientist observed eclipse
- Russia expedition
- Baja California, La Paz. Prof. Druckmüller's eclipse photography site
- Baja California, Todos Santos. Prof. Druckmüller's eclipse photography site
- Reyna from La Paz, Baja California, Mexico
- www.noao.edu: Satellite view of eclipse
- APOD 7/16/1999, Solar Surfin', total eclipse corona, from Mauna Kea, Hawaii
- APOD 10/24/1995, A Total Solar Eclipse, total eclipse corona
- The 1991 Eclipse in Mexico
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 1991 July 11. |
