Solar eclipse of September 12, 1950
| Solar eclipse of September 12, 1950 | |
|---|---|
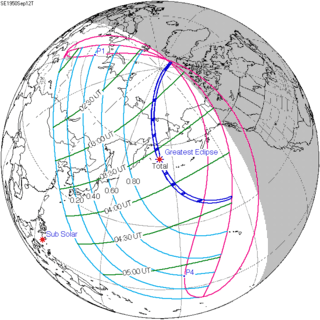 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | 0.8903 |
| Magnitude | 1.0182 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 74 sec (1 m 14 s) |
| Coordinates | 54°48′N 172°18′E / 54.8°N 172.3°E |
| Max. width of band | 134 km (83 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 3:38:47 |
| References | |
| Saros | 124 (51 of 73) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9399 |
A total solar eclipse occurred on September 12, 1950. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses of 1950-1953
Each member in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saros | Map | Saros | Map | |||
| 119 |  March 18, 1950 Annular |
124 |  September 12, 1950 Total | |||
| 129 |  March 7, 1951 Annular |
134 |  September 1, 1951 Annular | |||
| 139 | 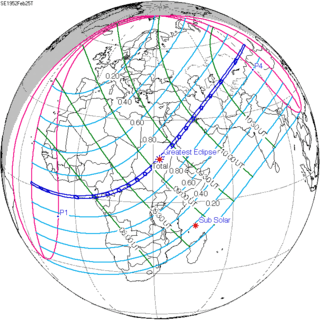 February 25, 1952 Total |
144 | 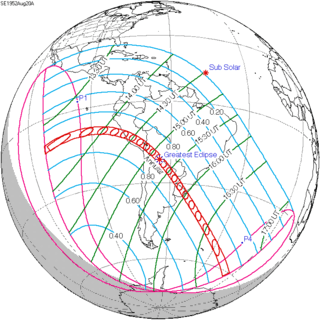 August 20, 1952 Annular | |||
| 149 | 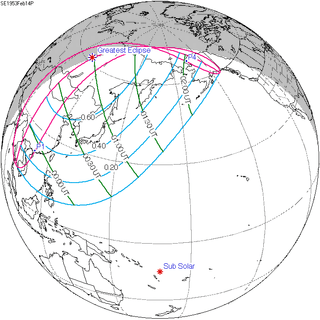 February 14, 1953 Partial |
154 |  August 9, 1953 Partial | |||
| Solar eclipse of July 11, 1953 belongs to the next lunar year set | ||||||
Notes
References
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 1950 September 12. |
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 1/15/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.
