Methyltestosterone
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Android, Androral, Metandren, Oraviron, Testred, Virilon |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | G03BA02 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Biological half-life | 6-8 hours |
| Excretion | 90% urine / 10% feces |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
58-18-4 |
| PubChem (CID) | 6010 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 6945 |
| DrugBank |
DB06710 |
| ChemSpider |
5788 |
| UNII |
V9EFU16ZIF |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:27436 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1395 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H30O2 |
| Molar mass | 302.451 |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
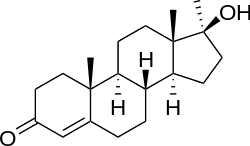
Methyltestosterone (brand names Android, Androral, Metandren, Oraviron, Testred, Virilon),[1] also known as 17α-methyltestosterone or as 17α-methylandrost-4-en-17β-ol-3-one, is a synthetic, orally active androgenic-anabolic steroid (AAS) and 17α-methylated derivative of testosterone that is used to treat males with androgen deficiency.[2] It bears close structural similarity to testosterone, but has a methyl group at the C17α position in order to increase oral bioavailability. Due to efficient aromatization into the potent estrogen methylestradiol, methyltestosterone has relatively high estrogenicity and hence potential side effects such as gynecomastia.[3][4]

History
Methyltestosterone was first synthesized in 1935, and was the first 17α-alkylated AAS to be synthesized.[5]
See also
- List of androgens/anabolic steroids
- Ethyltestosterone
- Topterone
- 17α-Methylprogesterone
- Ethinyl estradiol
- Metandienone
- Methylestradiol
- Normethandrone
References
- ↑ "Methyltestosterone Oral : Uses, Side Effects, Interactions, Pictures, Warnings & Dosing". WebMD. Retrieved 2012-02-13.
- ↑ "Truestar health".
- ↑ Detlef Thieme; Peter Hemmersbach (18 December 2009). Doping in Sports. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 470–. ISBN 978-3-540-79088-4.
- ↑ Andrea R. Genazzani (17 January 2006). Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: Hormones & Other Therapies. Taylor & Francis US. pp. 243–. ISBN 978-1-84214-311-7.
- ↑ Shahidi NT (2001). "A review of the chemistry, biological action, and clinical applications of anabolic-androgenic steroids". Clin Ther. 23 (9): 1355–90. PMID 11589254.
| AR |
| ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPRC6A |
| ||||||||||
See also: Estrogenics • Glucocorticoidics • Mineralocorticoidics • Progestogenics • Steroid hormone metabolism modulators • List of androgens/anabolic steroids | |||||||||||
| ER |
| ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPER |
| ||||||||||
See also: Androgenics • Glucocorticoidics • Mineralocorticoidics • Progestogenics • Steroid hormone metabolism modulators | |||||||||||